APPS R12 LOG FILE LOCATIONS
Log files are useful in troubleshooting issues in Oracle Applications. Here is the list of Log file location in Oracle Applications for Startup/Shutdown, Cloning, Patching, DB & Apps Listener and various components in Apps R12/12i:
A. Startup/Shutdown Log files for Application Tier in R12
Instance Top is new TOP added in R12 (to read more click here)
–Startup/Shutdown error message text files like adapcctl.txt, adcmctl.txt…
$INST_TOP/apps/$CONTEXT_NAME/logs/appl/admin/log
–Startup/Shutdown error message related to tech stack (10.1.2, 10.1.3 forms/reports/web)
$INST_TOP/apps/$CONTEXT_NAME/logs/ora/ (10.1.2 & 10.1.3)
$INST_TOP/apps/$CONTEXT_NAME/logs/ora/10.1.3/Apache/error_log[timestamp]
$INST_TOP/apps/$CONTEXT_NAME/logs/ora/10.1.3/opmn/ (OC4J~…, oa*, opmn.log)$INST_TOP/apps/$CONTEXT_NAME/logs/ora/10.1.2/network/ (listener log)
$INST_TOP/apps/$CONTEXT_NAME/logs/appl/conc/log (CM log files)
B. Log files related to cloning in R12
Preclone log files in source instance
i) Database Tier - /$ORACLE_HOME/appsutil/log/$CONTEXT_NAME/(StageDBTier_MMDDHHMM.log)
ii) Application Tier - $INST_TOP/apps/$CONTEXT_NAME/admin/log/ (StageAppsTier_MMDDHHMM.log)
Clone log files in target instance
Database Tier - $ORACLE_HOME/appsutil/log/$CONTEXT_NAME/ApplyDBTier_
Thursday, June 19, 2008
MULTI NODE TO SINGLE NODE CLONING
Multi Node to Single Node Cloning
With Oracle Applications 11.5.10 the ability to clone from a multi node to a single node system using rapid clone has now been certified.
This is accomplished by the Shared APPL_TOP and Merging APPL_TOP features.
In this post i am listing out the steps to perform a multi note to a single node cloning from scratch. The information mentioned here is the steps which i have used and found them to be successful for a more elaborate explanation you might want to refer to the metalink note Sharing the Application Tier File System in Oracle E-Business Suite 11i (233428.1).
Source System here refers to the multi node system to be cloned
Target System refers to the newly to be created single node system
Applications Version 11.5.10
Operating System Linux ES 4
The following Steps are required to be performed on the source system
1. Apply application tier patches using adpatch
Apply patch 4038964
Apply patch 4175764
Both the above patches are include in the consolidated update 2 or CU2 so in case you are on 11.5.10.2 or later you can ignore this step.
2. Maintain snapshot information
Log in as the applications user on each application tier node and run 'Maintain Snapshot Information' by using adadmin.
3. Merge existing APPL_TOPs
Log in to the primary node of your application tier as the application user user and run:
$ cd [COMMON_TOP]/admin/scripts/[CONTEXT_NAME]
$ perl adpreclone.pl appsTier merge
This will prompt you with option to merge secondary nodes
Now log in as the applications user to each of the secondary application tier nodes being merged and run:
$ cd [COMMON_TOP]/admin/scripts/[CONTEXT_NAME]
$ perl adpreclone.pl appltop merge
4. Prepare the source system database tier.
Log on to the database tier of the source system as the oracle user and run the following commands:
$ cd [RDBMS ORACLE_HOME]/appsutil/scripts/[CONTEXT_NAME]
$ perl adpreclone.pl dbTier
With this all the pre clone tasks on the source system have been completed.
The next set of tasks are required to be carried out on the target system that is the system on which you wish to place the merged single node instance.
1. Create OS user accounts
Create a OS user account for your applications
$ useradd -g dba -d [home_directory] -p password username
Similarly create a OS user account for your database
2. Modify the orainventory to reflect the new location
$ vi /etc/oraInst.loc
3. Copy the following application tier directories
Copy the following application tier directories from the primary node of your source system to the target application tier node, retaining the original directory structure:
– [APPL_TOP]
– [OA_HTML]
– [OA_JAVA]
– [COMMON_TOP/util]
– [COMMON_TOP/clone>
– [806 ORACLE_HOME]
– [iAS ORACLE_HOME]
4. Copy the required files for merging
Log in as the applications user to each of the secondary source nodes and recursively copy:
directory [COMMON_TOP]/clone/appl
- to -
directory [COMMMON_TOP]/clone/appl on the target system node
Before proceeding with the next steps you must shutdown your oracle applications services and the database on the source system
5. Copy the database tier file system
Log on to the source system as the database user
Copy the database (DBF) files from the source to the target system
Copy the source database ORACLE_HOME to the target system
After this you can now startup the database and applications services on your source system and release it for use.
6. Configure the target system database server
Log on to the target system as the database user and type the following commands to configure and start the database:
$ cd [RDBMS ORACLE_HOME]/appsutil/clone/bin
$ perl adcfgclone.pl dbTier
This will prompt for new ORACLE_SID,ORACLE_HOME,Port Pool,JAVA_TOP and DATA_TOP give the appropriate values matching your target system
Once successful this should start your database and listener
7. Configure the application tier server nodes
The database and its listener should remain up before executing the next set of commands.
Log in to the merged APPL_TOP node as the applications user and execute the following commands:
$ cd [COMMON_TOP]/clone/bin
$ perl adcfgclone.pl appsTier
This will prompt you new port pool for applictaion tier services as well as new APPLTOP,COMMON_TOP,ORACLE_HOME and IAS_TOP
Successful completion of this task will bring up your application tier services on the target or the cloned node.
8. Post Clone Tasks
Log in to the target system application tier node as the APPLMGR user.
Run the following tasks in adadmin for all products:
o generate JAR files
o generate message files
o relink executables
o copy files to destination
9. Clean up of the target system
Remove the temporary directory [COMMON_TOP]/clone/appl to reduce disk space usage.
Note: The version of Oracle Applications used is 11.5.10 and the operating system is Linux ES 4
With Oracle Applications 11.5.10 the ability to clone from a multi node to a single node system using rapid clone has now been certified.
This is accomplished by the Shared APPL_TOP and Merging APPL_TOP features.
In this post i am listing out the steps to perform a multi note to a single node cloning from scratch. The information mentioned here is the steps which i have used and found them to be successful for a more elaborate explanation you might want to refer to the metalink note Sharing the Application Tier File System in Oracle E-Business Suite 11i (233428.1).
Source System here refers to the multi node system to be cloned
Target System refers to the newly to be created single node system
Applications Version 11.5.10
Operating System Linux ES 4
The following Steps are required to be performed on the source system
1. Apply application tier patches using adpatch
Apply patch 4038964
Apply patch 4175764
Both the above patches are include in the consolidated update 2 or CU2 so in case you are on 11.5.10.2 or later you can ignore this step.
2. Maintain snapshot information
Log in as the applications user on each application tier node and run 'Maintain Snapshot Information' by using adadmin.
3. Merge existing APPL_TOPs
Log in to the primary node of your application tier as the application user user and run:
$ cd [COMMON_TOP]/admin/scripts/[CONTEXT_NAME]
$ perl adpreclone.pl appsTier merge
This will prompt you with option to merge secondary nodes
Now log in as the applications user to each of the secondary application tier nodes being merged and run:
$ cd [COMMON_TOP]/admin/scripts/[CONTEXT_NAME]
$ perl adpreclone.pl appltop merge
4. Prepare the source system database tier.
Log on to the database tier of the source system as the oracle user and run the following commands:
$ cd [RDBMS ORACLE_HOME]/appsutil/scripts/[CONTEXT_NAME]
$ perl adpreclone.pl dbTier
With this all the pre clone tasks on the source system have been completed.
The next set of tasks are required to be carried out on the target system that is the system on which you wish to place the merged single node instance.
1. Create OS user accounts
Create a OS user account for your applications
$ useradd -g dba -d [home_directory] -p password username
Similarly create a OS user account for your database
2. Modify the orainventory to reflect the new location
$ vi /etc/oraInst.loc
3. Copy the following application tier directories
Copy the following application tier directories from the primary node of your source system to the target application tier node, retaining the original directory structure:
– [APPL_TOP]
– [OA_HTML]
– [OA_JAVA]
– [COMMON_TOP/util]
– [COMMON_TOP/clone>
– [806 ORACLE_HOME]
– [iAS ORACLE_HOME]
4. Copy the required files for merging
Log in as the applications user to each of the secondary source nodes and recursively copy:
directory [COMMON_TOP]/clone/appl
- to -
directory [COMMMON_TOP]/clone/appl on the target system node
Before proceeding with the next steps you must shutdown your oracle applications services and the database on the source system
5. Copy the database tier file system
Log on to the source system as the database user
Copy the database (DBF) files from the source to the target system
Copy the source database ORACLE_HOME to the target system
After this you can now startup the database and applications services on your source system and release it for use.
6. Configure the target system database server
Log on to the target system as the database user and type the following commands to configure and start the database:
$ cd [RDBMS ORACLE_HOME]/appsutil/clone/bin
$ perl adcfgclone.pl dbTier
This will prompt for new ORACLE_SID,ORACLE_HOME,Port Pool,JAVA_TOP and DATA_TOP give the appropriate values matching your target system
Once successful this should start your database and listener
7. Configure the application tier server nodes
The database and its listener should remain up before executing the next set of commands.
Log in to the merged APPL_TOP node as the applications user and execute the following commands:
$ cd [COMMON_TOP]/clone/bin
$ perl adcfgclone.pl appsTier
This will prompt you new port pool for applictaion tier services as well as new APPLTOP,COMMON_TOP,ORACLE_HOME and IAS_TOP
Successful completion of this task will bring up your application tier services on the target or the cloned node.
8. Post Clone Tasks
Log in to the target system application tier node as the APPLMGR user.
Run the following tasks in adadmin for all products:
o generate JAR files
o generate message files
o relink executables
o copy files to destination
9. Clean up of the target system
Remove the temporary directory [COMMON_TOP]/clone/appl to reduce disk space usage.
Note: The version of Oracle Applications used is 11.5.10 and the operating system is Linux ES 4
MANUALLY CLONE DATABASE
MANUALLY CLONE DATABASE
To clone a database manually, we need first use the operating system(OS) to copy all of the source database files to the target location.
If we are on the same server we need to change the name of the database. If we are on a different server we can keep the database name as it is.
We should first backup the source database control file to trace using the statement
SQL>ALTER DATABASE BACKUP CONTROLFILE TO TRACE;
Using the trace file contents create a new control file that will help us create the new clone database.
Steps to Manually Clone a Database :
We follow the steps given below assuming that our source database is the production database named "prod" and our destination (target) database is the database named "test".
1) Copy the prod database files to the target location
2) Prepare a text file for the creation of a control file or the new database as follows :
SQL> ALTER DATABASE BACKUP CONTROLFILE TO TRACE;
3) On the target location, create all the directories for the various files
4) Copy the following four sets of files from the production(source) database to the target database :
parameter files
control files
data files
redo log files
5) In all the clone database files, change the database name to test
6) Run the CREATE DATABASE statement,which was prepared with the ALTER DATABASE BACKUP CONTROLFILE TO TRACE statement
7) Create the controlfile for the test database using the following statement:
SQL> CREATE CONTROLFILE REUSE SET DATABASE "TEST" RESETLOGS
NOARCHIVELOG;
We'll now have a new database called test that has a new controlfile pointing to the copied(target) version of the production database
8) Once we get the prompt back from the previous command, run this command :
SQL> ALTER DATABASE OPEN RESETLOGS USING BACKUP CONTROLFILE;
9) Finally, change the global name of the database we just created by running the following command:
SQL> UPDATE global_name SQT global_name='test.world';
To clone a database manually, we need first use the operating system(OS) to copy all of the source database files to the target location.
If we are on the same server we need to change the name of the database. If we are on a different server we can keep the database name as it is.
We should first backup the source database control file to trace using the statement
SQL>ALTER DATABASE BACKUP CONTROLFILE TO TRACE;
Using the trace file contents create a new control file that will help us create the new clone database.
Steps to Manually Clone a Database :
We follow the steps given below assuming that our source database is the production database named "prod" and our destination (target) database is the database named "test".
1) Copy the prod database files to the target location
2) Prepare a text file for the creation of a control file or the new database as follows :
SQL> ALTER DATABASE BACKUP CONTROLFILE TO TRACE;
3) On the target location, create all the directories for the various files
4) Copy the following four sets of files from the production(source) database to the target database :
parameter files
control files
data files
redo log files
5) In all the clone database files, change the database name to test
6) Run the CREATE DATABASE statement,which was prepared with the ALTER DATABASE BACKUP CONTROLFILE TO TRACE statement
7) Create the controlfile for the test database using the following statement:
SQL> CREATE CONTROLFILE REUSE SET DATABASE "TEST" RESETLOGS
NOARCHIVELOG;
We'll now have a new database called test that has a new controlfile pointing to the copied(target) version of the production database
8) Once we get the prompt back from the previous command, run this command :
SQL> ALTER DATABASE OPEN RESETLOGS USING BACKUP CONTROLFILE;
9) Finally, change the global name of the database we just created by running the following command:
SQL> UPDATE global_name SQT global_name='test.world';
Saturday, June 14, 2008
IMPORTANT METALINK NOTES
IMPORTANT Metalink Notes
I was recently plugged on to one of the podcasts by Steven Chan, in which he described his experiences on running his extremely popular blog on Oracle Applications Technology. An interesting observation pointed out here by Steven was that one of the principle driving object of his blog was that, the metalink which contained a wealth of information was still outside the internet search engine's indexing.
Since metalink does not allow the search engines to index its content due to understandable security concerns, There is a significant percentage of the Oracle Applications Community who Google. Obviously even if the information they are looking out for is available it gets missed out form there search results.
By creating pointers or references to the metalink notes in his blog. It has enabled this information to have wider exposure since his blog is obviously indexed by the search engines, so as the information contained within.
The current post is my bit of effort to carry out this task by listing out a few of my favorite Metalink Notes relating to Oracle Applications.
Please do remember you must have a valid metalink account to access these notes. Also the notes are copyrighted by Oracle and a great amount of time and effort has been put into them, publishing or distributing them is not allowed and more importantly not rite!
Applications FAQ
* Note Id:285267.1 Oracle E-Business Suite 11i and Database FAQ
* Note Id:177610.1 Oracle Forms in Applications FAQ
Cloning
* Note Id:216664.1 FAQ: Cloning Oracle Applications Release 11i
* Note Id:230672.1 Cloning Oracle Applications Release 11i with Rapid Clone
* Note Id:364565.1 Troubleshooting RapidClone issues with Oracle Applications 11i
* Note Id:398619.1 Clone Oracle Applications 11i using Oracle Application Manager (OAM Clone)
Oracle Applications with Oracle Application Server
* Note Id:186981.1 Oracle Application Server with Oracle E-Business Suite Release 11i FAQ
* Note Id:233436.1 Installing Oracle Application Server 10g with Oracle E-Business Suite Release 11i
* Note Id:295606.1 Oracle Application Server 10g with Oracle E-Business Suite Release 11i Troubleshooting
Autoconfig
* Note Id:218089.1 Autoconfig FAQ
* Note Id:315674.1 How To Verify if Autoconfig is Enabled on 11.5.x
* Note Id:165195.1 Using AutoConfig to Manage System Configurations with Oracle Applications 11i
* Note Id:341322.1 How to change the hostname of an Applications Tier using AutoConfig
* Note Id:270519.1 Customizing an AutoConfig Environment
Oracle Applications and Database
* Note Id:362203.1 Oracle Applications Release 11i with Oracle 10g Release 2 (10.2.0)
Oracle Applications And RAC
* Note Id:220970.1 RAC: Frequently Asked Questions
* Note Id:294652.1 E-Business Suite 11i on RAC : Configuring Database Load balancing & Failover
* Note Id:312731.1 Configuring Oracle Applications Release 11i with 10g RAC and 10g ASM
DMZ with Oracle Applications
* Note Id:287176.1 DMZ Configuration with Oracle E-Business Suite 11i
* Note Id:377856.1 DMZ Reverse Proxy and Middle Tier In Different Domains
SSL and Oracle Applications
* Note Id:123718.1 11i: A Guide to Understanding and Implementing SSL for Oracle Applications
* Note Id:340178.1 Enabling SSL with Oracle Application Server 10g and the E-Business Suite
Shared APPL_TOP and Application Tier Filesystem
* Note Id:243880.1 Shared APPL_TOP FAQ
* Note Id:233428.1 Sharing the Application Tier File System in Oracle Applications 11i
Patching
* Note Id:174436.1 Oracle Applications Patching FAQ
* Note Id:224875.1 Installation, Patching & Upgrade Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ's)
* Note Id:139684.1 Oracle Applications Current Patchset Comparison Utility - patchsets.sh
* Note Id:374915.1 HRMS PATCH INSTALL FAQ
* Note Id:130608.1 ADPATCH BASICS
* Note Id:314540.1 What Log Files are Generated with Adpatch, and Where are They Located?
* Note Id:229423.1 Troubleshooting adpatch complaining of apps.zip existence issues
* Note Id:136342.1 How To Apply a Patch in a Multi-Server Environment
Concurrent Managers
* Note Id:69336.1 Basic information about Concurrent Managers
* Note Id:105133.1 Concurrent Manager Questions and Answers Relating to Generic Platform
* Note Id:241370.1 Concurrent Manager Setup and Configuration Requirements in an 11i RAC Environment
* Note Id:210062.1 Generic Service Management (GSM) in Oracle Applications 11i
System Administration
* Note Id:189487.1 System Administration FAQ's
Troubleshooting
* Note Id:342332.1 Troubleshooting Login Problems in Oracle Applications 11i (11.5.2 – 11.5.10+)
* Note Id:104531.1 Troubleshooting (Report Review Agent)
Portal with Oracle Applications
* Note Id:305918.1 Using Oracle Portal 10g with Oracle E-Business Suite 11i
Single Sign-On with Oracle Applications
* Note Id:233436.1 Installing Oracle Application Server 10g with Oracle E-Business Suite Release 11i
* Note Id:114534.996 OFA Single Sign-on through Apps 11i
* Note Id:295606.1 Troubleshooting SSO with Oracle Applications
I was recently plugged on to one of the podcasts by Steven Chan, in which he described his experiences on running his extremely popular blog on Oracle Applications Technology. An interesting observation pointed out here by Steven was that one of the principle driving object of his blog was that, the metalink which contained a wealth of information was still outside the internet search engine's indexing.
Since metalink does not allow the search engines to index its content due to understandable security concerns, There is a significant percentage of the Oracle Applications Community who Google. Obviously even if the information they are looking out for is available it gets missed out form there search results.
By creating pointers or references to the metalink notes in his blog. It has enabled this information to have wider exposure since his blog is obviously indexed by the search engines, so as the information contained within.
The current post is my bit of effort to carry out this task by listing out a few of my favorite Metalink Notes relating to Oracle Applications.
Please do remember you must have a valid metalink account to access these notes. Also the notes are copyrighted by Oracle and a great amount of time and effort has been put into them, publishing or distributing them is not allowed and more importantly not rite!
Applications FAQ
* Note Id:285267.1 Oracle E-Business Suite 11i and Database FAQ
* Note Id:177610.1 Oracle Forms in Applications FAQ
Cloning
* Note Id:216664.1 FAQ: Cloning Oracle Applications Release 11i
* Note Id:230672.1 Cloning Oracle Applications Release 11i with Rapid Clone
* Note Id:364565.1 Troubleshooting RapidClone issues with Oracle Applications 11i
* Note Id:398619.1 Clone Oracle Applications 11i using Oracle Application Manager (OAM Clone)
Oracle Applications with Oracle Application Server
* Note Id:186981.1 Oracle Application Server with Oracle E-Business Suite Release 11i FAQ
* Note Id:233436.1 Installing Oracle Application Server 10g with Oracle E-Business Suite Release 11i
* Note Id:295606.1 Oracle Application Server 10g with Oracle E-Business Suite Release 11i Troubleshooting
Autoconfig
* Note Id:218089.1 Autoconfig FAQ
* Note Id:315674.1 How To Verify if Autoconfig is Enabled on 11.5.x
* Note Id:165195.1 Using AutoConfig to Manage System Configurations with Oracle Applications 11i
* Note Id:341322.1 How to change the hostname of an Applications Tier using AutoConfig
* Note Id:270519.1 Customizing an AutoConfig Environment
Oracle Applications and Database
* Note Id:362203.1 Oracle Applications Release 11i with Oracle 10g Release 2 (10.2.0)
Oracle Applications And RAC
* Note Id:220970.1 RAC: Frequently Asked Questions
* Note Id:294652.1 E-Business Suite 11i on RAC : Configuring Database Load balancing & Failover
* Note Id:312731.1 Configuring Oracle Applications Release 11i with 10g RAC and 10g ASM
DMZ with Oracle Applications
* Note Id:287176.1 DMZ Configuration with Oracle E-Business Suite 11i
* Note Id:377856.1 DMZ Reverse Proxy and Middle Tier In Different Domains
SSL and Oracle Applications
* Note Id:123718.1 11i: A Guide to Understanding and Implementing SSL for Oracle Applications
* Note Id:340178.1 Enabling SSL with Oracle Application Server 10g and the E-Business Suite
Shared APPL_TOP and Application Tier Filesystem
* Note Id:243880.1 Shared APPL_TOP FAQ
* Note Id:233428.1 Sharing the Application Tier File System in Oracle Applications 11i
Patching
* Note Id:174436.1 Oracle Applications Patching FAQ
* Note Id:224875.1 Installation, Patching & Upgrade Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ's)
* Note Id:139684.1 Oracle Applications Current Patchset Comparison Utility - patchsets.sh
* Note Id:374915.1 HRMS PATCH INSTALL FAQ
* Note Id:130608.1 ADPATCH BASICS
* Note Id:314540.1 What Log Files are Generated with Adpatch, and Where are They Located?
* Note Id:229423.1 Troubleshooting adpatch complaining of apps.zip existence issues
* Note Id:136342.1 How To Apply a Patch in a Multi-Server Environment
Concurrent Managers
* Note Id:69336.1 Basic information about Concurrent Managers
* Note Id:105133.1 Concurrent Manager Questions and Answers Relating to Generic Platform
* Note Id:241370.1 Concurrent Manager Setup and Configuration Requirements in an 11i RAC Environment
* Note Id:210062.1 Generic Service Management (GSM) in Oracle Applications 11i
System Administration
* Note Id:189487.1 System Administration FAQ's
Troubleshooting
* Note Id:342332.1 Troubleshooting Login Problems in Oracle Applications 11i (11.5.2 – 11.5.10+)
* Note Id:104531.1 Troubleshooting (Report Review Agent)
Portal with Oracle Applications
* Note Id:305918.1 Using Oracle Portal 10g with Oracle E-Business Suite 11i
Single Sign-On with Oracle Applications
* Note Id:233436.1 Installing Oracle Application Server 10g with Oracle E-Business Suite Release 11i
* Note Id:114534.996 OFA Single Sign-on through Apps 11i
* Note Id:295606.1 Troubleshooting SSO with Oracle Applications
MANAGING YOUR 10g APPLICATION SERVER
Managing Your 10g Application Server
After having discussed about installation and configuration of Oracle Applications Server, in today’s post I will talk about managing the application server primarily the startup and shutdown procedures. I am sure this would have been already well documented by oracle but the post aims summing up the process. I will discuss the opmn tool by Oracle and also the Enterprise Manager
The process described here also holds good for other Oracle products like Oracle Collaboration suite and Oracle SOA suite.
Any application server would necessarily consist of a infrastructure Tier, it may or may not have a middle tier associated.
Starting Application Server Services
Order of Startup
As the middle tier is dependent on your infrastructure it is important that the infrastructure should be up and running before you proceed with the middle tier services.
Using runstartupconsole.sh
You can start up the infrastructure tier services using the runstartupconsole.sh script located at your $ORACLE_HOME/bin/ on the machine which contains your infrastructure.
# su - saminf
$ cd $ORACLE_HOME/bin
$runstartupconsole.sh start
This command will startup
The AS Meta Data Repository Instance
The Listener
The Enterprise Manager Console
Infrastructure Process Such as OID,OC4J_security,SSO etc.
To startup the middle Tier Services you log in to your middle tier OS user and run the the runstartupconsole.sh from the middle tier ORACLE_HOME.
# su - sammid
$ cd $ORACLE_HOME/bin
$runstartupconsole.sh start
This Command will start up
The 10g Enterprise Manager
All OPMN managed process for the middle tier like portal
Using Enterprise Manager Console
You can also use the 10g Enterprise Manager console to start up the infrastructure tier and middle tier services, however you must start up the enterprise manager explicitly before you can use it. The emctl command is used to startup the enterprise manager. The location is $ORACLE_HOME/bin
#su - saminf
$emctl start iasconsole
You can logon top the enterprise manager using the ias_admin username and password given at the time of installatiuon. You can get the URL of the EM from the setupinfo.txt file located at the $ORACLE_HOME/install directory location.
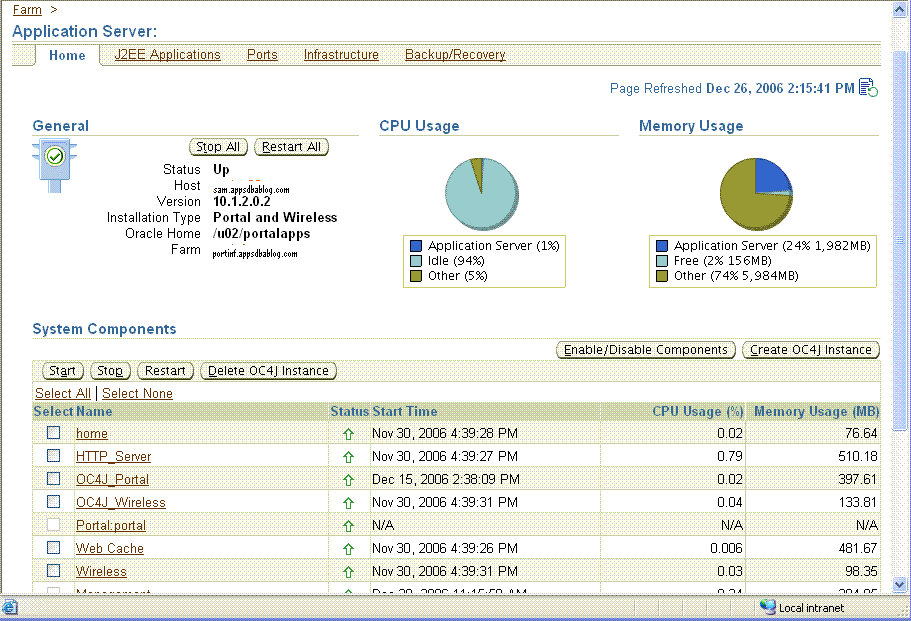
Similarly you can start the EM of the middle Tier using the emctl command and start the middle tier services using the EM console.
However you must start your Meta Data Repository instance and Listener manually before starting and using the EM console.
Using OPMN
OPMN stands for the Oracle Process Manager and Notification, is a tool with you can manage the OPMN managed Infrastructure and Middle Tier Porcess. The opmnctl executable is located at the $ORACLE_HOME/opmn/bin.
opmnctl start
This command will start up your opmn process
opmnctl startall
This will start up the opmn process and all process managed by opmn
opmnctl startporc ias-component=component
This will start a specific opmn managed process like SSO
You can also start using the sub-porcess of a component using
opmnctl startproc process-type=process
You could also restart the processs using
opmnctl restartproc ias-component=component
opmnctl restartproc process-type=process
However before using OPMNCTL you must have started your Metadata Respositery Database Instance and the Listener manually.
Shutdown of Application Tier Services
Order Of Shutdown
Your Middle tier Services must be shutdown before you shutdown your infrastructure services.
Using runstartupconsole.sh
You can shutdown the infrastructure tier services using the runstartupconsole.sh script located at your $ORACLE_HOME/bin/ on the machine which contains your infrastructure.
# su - saminf
$ cd $ORACLE_HOME/bin
$runstartupconsole.sh stop
This command will stop
All infrastructure tier services
The 10g EM console
The meta data repository instance
The listener
For middle Tier services you must run this command for the middle tier ORACLE_HOME.
Using Enterprise Manager Console
You can also use the 10g EM console to shutdown your middle tier and infrastructure services.
After that you must shutdown your EM console manually using the emctl command
emctl stop iasconsole
You can also shutdown the Infrastructure services using the EM Console of the infrastructure tier after which you must manually shutdown the EM console manually using emctl at the infrastructure tier.
You must also remember to bring down your Meta Data Repository and Listener manually from the infrastructure home after all the services are brought down.
Using OPMN
Using opmnctl you can shutdown your middle tier services and infrastructure services.
opmnctl shutdown
This shutdown the opmn process and along with it all the managed opmn processes
opmnctl stopall
This command stops all opmn managed process for a particular tier.
You can also stop a specify OPMN managed component using
opmnctl stopproc ias-component=component
or
opmnctl stopproc process-type=process
The EM console on the middle tier and the infrastructure tier needs to be brought down manually using emctl stop iasconsole.
Also the Meta Data Repository Instance and Listener need to be brought down manually.
After having discussed about installation and configuration of Oracle Applications Server, in today’s post I will talk about managing the application server primarily the startup and shutdown procedures. I am sure this would have been already well documented by oracle but the post aims summing up the process. I will discuss the opmn tool by Oracle and also the Enterprise Manager
The process described here also holds good for other Oracle products like Oracle Collaboration suite and Oracle SOA suite.
Any application server would necessarily consist of a infrastructure Tier, it may or may not have a middle tier associated.
Starting Application Server Services
Order of Startup
As the middle tier is dependent on your infrastructure it is important that the infrastructure should be up and running before you proceed with the middle tier services.
Using runstartupconsole.sh
You can start up the infrastructure tier services using the runstartupconsole.sh script located at your $ORACLE_HOME/bin/ on the machine which contains your infrastructure.
# su - saminf
$ cd $ORACLE_HOME/bin
$runstartupconsole.sh start
This command will startup
The AS Meta Data Repository Instance
The Listener
The Enterprise Manager Console
Infrastructure Process Such as OID,OC4J_security,SSO etc.
To startup the middle Tier Services you log in to your middle tier OS user and run the the runstartupconsole.sh from the middle tier ORACLE_HOME.
# su - sammid
$ cd $ORACLE_HOME/bin
$runstartupconsole.sh start
This Command will start up
The 10g Enterprise Manager
All OPMN managed process for the middle tier like portal
Using Enterprise Manager Console
You can also use the 10g Enterprise Manager console to start up the infrastructure tier and middle tier services, however you must start up the enterprise manager explicitly before you can use it. The emctl command is used to startup the enterprise manager. The location is $ORACLE_HOME/bin
#su - saminf
$emctl start iasconsole
You can logon top the enterprise manager using the ias_admin username and password given at the time of installatiuon. You can get the URL of the EM from the setupinfo.txt file located at the $ORACLE_HOME/install directory location.
Similarly you can start the EM of the middle Tier using the emctl command and start the middle tier services using the EM console.
However you must start your Meta Data Repository instance and Listener manually before starting and using the EM console.
Using OPMN
OPMN stands for the Oracle Process Manager and Notification, is a tool with you can manage the OPMN managed Infrastructure and Middle Tier Porcess. The opmnctl executable is located at the $ORACLE_HOME/opmn/bin.
opmnctl start
This command will start up your opmn process
opmnctl startall
This will start up the opmn process and all process managed by opmn
opmnctl startporc ias-component=component
This will start a specific opmn managed process like SSO
You can also start using the sub-porcess of a component using
opmnctl startproc process-type=process
You could also restart the processs using
opmnctl restartproc ias-component=component
opmnctl restartproc process-type=process
However before using OPMNCTL you must have started your Metadata Respositery Database Instance and the Listener manually.
Shutdown of Application Tier Services
Order Of Shutdown
Your Middle tier Services must be shutdown before you shutdown your infrastructure services.
Using runstartupconsole.sh
You can shutdown the infrastructure tier services using the runstartupconsole.sh script located at your $ORACLE_HOME/bin/ on the machine which contains your infrastructure.
# su - saminf
$ cd $ORACLE_HOME/bin
$runstartupconsole.sh stop
This command will stop
All infrastructure tier services
The 10g EM console
The meta data repository instance
The listener
For middle Tier services you must run this command for the middle tier ORACLE_HOME.
Using Enterprise Manager Console
You can also use the 10g EM console to shutdown your middle tier and infrastructure services.
After that you must shutdown your EM console manually using the emctl command
emctl stop iasconsole
You can also shutdown the Infrastructure services using the EM Console of the infrastructure tier after which you must manually shutdown the EM console manually using emctl at the infrastructure tier.
You must also remember to bring down your Meta Data Repository and Listener manually from the infrastructure home after all the services are brought down.
Using OPMN
Using opmnctl you can shutdown your middle tier services and infrastructure services.
opmnctl shutdown
This shutdown the opmn process and along with it all the managed opmn processes
opmnctl stopall
This command stops all opmn managed process for a particular tier.
You can also stop a specify OPMN managed component using
opmnctl stopproc ias-component=component
or
opmnctl stopproc process-type=process
The EM console on the middle tier and the infrastructure tier needs to be brought down manually using emctl stop iasconsole.
Also the Meta Data Repository Instance and Listener need to be brought down manually.
CONFIGURING SINGLE SIGN ON WITH ORACLE APPLICATION (Linux AS)
Configuring Single Sign On With Oracle Application (Linux AS)
In my last post i has discussed about Single Sign On in Oracle Applications, This post focuses on detail step by step instructions for configuring single Sign On With an existing Oracle Applications Instance.
This is assuming that you already have a Oracle Applications instance and a 10 G Application Server instance installed.
System Overview
Oracle Applications
Version 11.5.10.2
OS: Redhat Linux
Type: Single Node instance (Node A)
Applications OS User: applsam
Database OS User : orasam
Instance SID: SAM
Host: Node A
Port Pool: 23
10g Application Server
Version: 10.1.2.0
OS: Redhat Linux
Infrastructure with the following configured components
OracleAS Metadata Repository
Oracle HTTP Server
OracleAS Containers for J2EE
Oracle Internet Directory
OracleAS Single Sign-On
OracleAS Delegated Administration Service
OracleAS Directory Integration and Provisioning
OS user for infrastructure: saminf
ORACLE_HOME: /u01/sam/saminf/OraHome
ORACLE SID: SAMAS
Host: Node B
Task: To implement SSO with Oracle Applications.
Pre requisite for Oracle Applications
Check the Apache version of your Oracle Applications on Node A
Log in as the applications user 'applsam'
$cd $IAS_ORACLE_HOME/Apache/Apache/bin
$./httpd -v
Server version: Oracle HTTP Server Powered by Apache/1.3.19 (Unix)
Server built: Feb 22 2005 18:51:19 (iAS 1.0.2.2.2 rollup 5)
If the version reported is less that 1.3.19 then you must apply Oracle9i Application Server Release 1.0.2.2.2 CD Pack.
Autoconfig
Make sure that your Oracle Applications is autoconfig enabled
DBMS_LDAP on E-Business Suite
Check if the DBMS_LDAP package is installed in your applications database.
Login is as the database user 'orasam'
$sqlplus "/ as sysdba"
SQL*Plus: Release 9.2.0.6.0 - Production on Fri Nov 3 10:23:38 2006
Copyright (c) 1982, 2002, Oracle Corporation. All rights reserved.
Connected to:
Oracle9i Enterprise Edition Release 9.2.0.6.0 - Production
With the Partitioning, OLAP and Oracle Data Mining options
JServer Release 9.2.0.6.0 - Production
SQL> desc DBMS_LDAP;
If the package does not exist create it using the catldap.sql located in $ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin/ as SYSDBA
Pre requisite for Oracle Application Server 10g
Release 10.1.2
If the version of Applications server is not 10.1.2 you must upgrade your 10 g application server to 10.1.2.0
Test OIDDAS
Log into to OIDDAS as orcladmin user and create a test user to test the working of your application server installation.
http://.:/oiddas
Implementing SSO
E-Business Suite SSO 10g Integration Patch
Apply the E-Business Suite SSO 10g Integration Patch (4775907) to your Oracle Applications using adapatch. Before applying the above patch make sure that all the pre requisite patches specified in the patch readme are applied.
Execute the SSO registration script in Oracle Applications.
The SSO registration script is a perl script and registers your E-Business Suite with SSO and OID. It prompts for a list of parameters which you should have ready.
Parameter List
Hostname of 10g AS: samlnx03.appsdbablog.com
Port Of Application Server DB : 1521
Application Server Database : samas
OID LDAP Port : 3060
APPS user password : apps
Password for the ORASSO User : I0ds305V
(You can use the ldapsearch script located in the $ORACLE_HOME/bin/ of your Application Server 10g instance or from your Oracle Directory Manager client software, i use the client as its easy)
Password for the SYSTEM user of Oracle Application DB : manager
Password for the 'SSOSDK' on your Oracle Applications DB : SSOSDK
(The user will be created if it does not exist)
Password for the OID admin user orcladmin : admin123
Password with which you wish to register your E-Business Suite with OID :admin123
A valid Provisioning Profile Template : The default is ProvBiDirection.tmp,you can find additional templates at $FND_TOP/admin/template/
The SSO registration script by default uses a ProvBiDirection.tmp provisioning profile which is a BI directional Provisioning template, you can also provide a different provisioning template.
Additionally you must ensure that the perl from your IAS_ORACLE_HOME is in your application users profile and the version is 5.005 or higher.
$ which perl
~/samora/iAS/Apache/perl/bin/perl
$ perl -v
This is perl, version 5.005_03 built for i686-linux
Copyright 1987-1999, Larry Wall
Execute the txkrun.pl script
$ txkrun.pl -script=SetSSOReg
Enter the host name where Oracle iAS Infrastructure database is installed ? hcslnx03.satyam.com
Enter the Oracle iAS Infrastructure database port number ? 1521
Enter the Oracle iAS Infrastructure database SID ? samas
Enter the LDAP Port on Oracle Internet Directory server ? 3060
Enter Oracle E-Business apps database user password ? apps
Enter Oracle iAS Infrastructure database ORASSO schema password ? I0ds305V
Enter Oracle E-Business SYSTEM database user password ? manager
Enter E-Business Suite existing SSOSDK schema password or choose a password to use with the new SSOSDK schema if the schema does not exist ? ssosdk
Enter the Oracle Internet Directory Administrator (orcladmin) Bind password ? admin123
Enter the instance password that you would like to register this application instance with ? admin123
*** ALL THE FOLLOWING FILES ARE REQUIRED FOR RESOLVING RUNTIME ERRORS
*** Log File = /u02/sam/applsam/samcomn/rgf/SAM_hcslnx08/sso/txkSetSSOReg_Fri_Nov_3_15_27_47_2006.log
Program : /u02/sam/applsam/samappl/fnd/11.5.0/patch/115/bin/txkSetSSOReg.pl started @ Fri Nov 3 15:29:53 2006
*** Log File = /u02/sam/applsam/samcomn/rgf/SAM_hcslnx08/sso/txkSetSSOReg_Fri_Nov_3_15_27_47_2006.log
######################## WARNING
This application works with SSOSDK version 9.0.2 or higher. If lower version
(3.0.9) of SSOSDK was installed in your system and you have a registered
partner application, this process will remove the 3.0.9 version of the SSOSDK
schema and install the 9.0.2 version.
######################## WARNING
Beginning input parameter validation for SSO registration.
Beginning loading SSO SDK into database if necessary.
Loading of SSO SDK into database completed successfully.
Input parameter validation for SSO registration completed.
Beginning input parameter validation for OID registration.
Input parameters validation for OID registration completed.
BEGIN SSO REGISTRATION:
Beginning to register partner application.
Partner application has been registered successfully.
Single Sign-On partner application registered successfully.
BEGIN OID REGISTRATION:
Beginning to register Application and Service containers if necessary.
Application and Service containers were created successfully.
Beginning to register application in Oracle Internet Directory.
Registration of application in Oracle Internet Directory completed successfully.
Beginning to register instance password in Oracle Internet Directory.
Registration of instance password in Oracle Internet Directory completed successfully.
Beginning to test application registration in Oracle Internet Directory.
Testing of application registration in Oracle Internet Directory completed successfully.
Beginning to register provisioning profile in Oracle Internet Directory.
Registration of provisioning profile in Oracle Internet Directory completed successfully.
Application is now registered successfully with provisioning in Oracle Internet Directory.
End of /u02/sam/applsam/samappl/fnd/11.5.0/patch/115/bin/txkSetSSOReg.pl : No Errors encountered
Add your 10g AS to the list of trusted nodes in your E-Business Suite
With 11.5.10 and higher you need to add the 10 G application server mode as a trusted node withing your E-Business suite You can do this through your Oracle Applications Manager Oracle Applications Manager=>Applications Dashboard=>Security=>Manage Security Options. You need to run autoconfig after this and bounce your database listener.
Restart your HTTP listener.
Restart your Apache HTTP listener to have your SSO registration take effect.
You may need to apply additional patches based on the E-Business Suite products installed.
In my last post i has discussed about Single Sign On in Oracle Applications, This post focuses on detail step by step instructions for configuring single Sign On With an existing Oracle Applications Instance.
This is assuming that you already have a Oracle Applications instance and a 10 G Application Server instance installed.
System Overview
Oracle Applications
Version 11.5.10.2
OS: Redhat Linux
Type: Single Node instance (Node A)
Applications OS User: applsam
Database OS User : orasam
Instance SID: SAM
Host: Node A
Port Pool: 23
10g Application Server
Version: 10.1.2.0
OS: Redhat Linux
Infrastructure with the following configured components
OracleAS Metadata Repository
Oracle HTTP Server
OracleAS Containers for J2EE
Oracle Internet Directory
OracleAS Single Sign-On
OracleAS Delegated Administration Service
OracleAS Directory Integration and Provisioning
OS user for infrastructure: saminf
ORACLE_HOME: /u01/sam/saminf/OraHome
ORACLE SID: SAMAS
Host: Node B
Task: To implement SSO with Oracle Applications.
Pre requisite for Oracle Applications
Check the Apache version of your Oracle Applications on Node A
Log in as the applications user 'applsam'
$cd $IAS_ORACLE_HOME/Apache/Apache/bin
$./httpd -v
Server version: Oracle HTTP Server Powered by Apache/1.3.19 (Unix)
Server built: Feb 22 2005 18:51:19 (iAS 1.0.2.2.2 rollup 5)
If the version reported is less that 1.3.19 then you must apply Oracle9i Application Server Release 1.0.2.2.2 CD Pack.
Autoconfig
Make sure that your Oracle Applications is autoconfig enabled
DBMS_LDAP on E-Business Suite
Check if the DBMS_LDAP package is installed in your applications database.
Login is as the database user 'orasam'
$sqlplus "/ as sysdba"
SQL*Plus: Release 9.2.0.6.0 - Production on Fri Nov 3 10:23:38 2006
Copyright (c) 1982, 2002, Oracle Corporation. All rights reserved.
Connected to:
Oracle9i Enterprise Edition Release 9.2.0.6.0 - Production
With the Partitioning, OLAP and Oracle Data Mining options
JServer Release 9.2.0.6.0 - Production
SQL> desc DBMS_LDAP;
If the package does not exist create it using the catldap.sql located in $ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin/ as SYSDBA
Pre requisite for Oracle Application Server 10g
Release 10.1.2
If the version of Applications server is not 10.1.2 you must upgrade your 10 g application server to 10.1.2.0
Test OIDDAS
Log into to OIDDAS as orcladmin user and create a test user to test the working of your application server installation.
http://
Implementing SSO
E-Business Suite SSO 10g Integration Patch
Apply the E-Business Suite SSO 10g Integration Patch (4775907) to your Oracle Applications using adapatch. Before applying the above patch make sure that all the pre requisite patches specified in the patch readme are applied.
Execute the SSO registration script in Oracle Applications.
The SSO registration script is a perl script and registers your E-Business Suite with SSO and OID. It prompts for a list of parameters which you should have ready.
Parameter List
Hostname of 10g AS: samlnx03.appsdbablog.com
Port Of Application Server DB : 1521
Application Server Database : samas
OID LDAP Port : 3060
APPS user password : apps
Password for the ORASSO User : I0ds305V
(You can use the ldapsearch script located in the $ORACLE_HOME/bin/ of your Application Server 10g instance or from your Oracle Directory Manager client software, i use the client as its easy)
Password for the SYSTEM user of Oracle Application DB : manager
Password for the 'SSOSDK' on your Oracle Applications DB : SSOSDK
(The user will be created if it does not exist)
Password for the OID admin user orcladmin : admin123
Password with which you wish to register your E-Business Suite with OID :admin123
A valid Provisioning Profile Template : The default is ProvBiDirection.tmp,you can find additional templates at $FND_TOP/admin/template/
The SSO registration script by default uses a ProvBiDirection.tmp provisioning profile which is a BI directional Provisioning template, you can also provide a different provisioning template.
Additionally you must ensure that the perl from your IAS_ORACLE_HOME is in your application users profile and the version is 5.005 or higher.
$ which perl
~/samora/iAS/Apache/perl/bin/perl
$ perl -v
This is perl, version 5.005_03 built for i686-linux
Copyright 1987-1999, Larry Wall
Execute the txkrun.pl script
$ txkrun.pl -script=SetSSOReg
Enter the host name where Oracle iAS Infrastructure database is installed ? hcslnx03.satyam.com
Enter the Oracle iAS Infrastructure database port number ? 1521
Enter the Oracle iAS Infrastructure database SID ? samas
Enter the LDAP Port on Oracle Internet Directory server ? 3060
Enter Oracle E-Business apps database user password ? apps
Enter Oracle iAS Infrastructure database ORASSO schema password ? I0ds305V
Enter Oracle E-Business SYSTEM database user password ? manager
Enter E-Business Suite existing SSOSDK schema password or choose a password to use with the new SSOSDK schema if the schema does not exist ? ssosdk
Enter the Oracle Internet Directory Administrator (orcladmin) Bind password ? admin123
Enter the instance password that you would like to register this application instance with ? admin123
*** ALL THE FOLLOWING FILES ARE REQUIRED FOR RESOLVING RUNTIME ERRORS
*** Log File = /u02/sam/applsam/samcomn/rgf/SAM_hcslnx08/sso/txkSetSSOReg_Fri_Nov_3_15_27_47_2006.log
Program : /u02/sam/applsam/samappl/fnd/11.5.0/patch/115/bin/txkSetSSOReg.pl started @ Fri Nov 3 15:29:53 2006
*** Log File = /u02/sam/applsam/samcomn/rgf/SAM_hcslnx08/sso/txkSetSSOReg_Fri_Nov_3_15_27_47_2006.log
######################## WARNING
This application works with SSOSDK version 9.0.2 or higher. If lower version
(3.0.9) of SSOSDK was installed in your system and you have a registered
partner application, this process will remove the 3.0.9 version of the SSOSDK
schema and install the 9.0.2 version.
######################## WARNING
Beginning input parameter validation for SSO registration.
Beginning loading SSO SDK into database if necessary.
Loading of SSO SDK into database completed successfully.
Input parameter validation for SSO registration completed.
Beginning input parameter validation for OID registration.
Input parameters validation for OID registration completed.
BEGIN SSO REGISTRATION:
Beginning to register partner application.
Partner application has been registered successfully.
Single Sign-On partner application registered successfully.
BEGIN OID REGISTRATION:
Beginning to register Application and Service containers if necessary.
Application and Service containers were created successfully.
Beginning to register application in Oracle Internet Directory.
Registration of application in Oracle Internet Directory completed successfully.
Beginning to register instance password in Oracle Internet Directory.
Registration of instance password in Oracle Internet Directory completed successfully.
Beginning to test application registration in Oracle Internet Directory.
Testing of application registration in Oracle Internet Directory completed successfully.
Beginning to register provisioning profile in Oracle Internet Directory.
Registration of provisioning profile in Oracle Internet Directory completed successfully.
Application is now registered successfully with provisioning in Oracle Internet Directory.
End of /u02/sam/applsam/samappl/fnd/11.5.0/patch/115/bin/txkSetSSOReg.pl : No Errors encountered
Add your 10g AS to the list of trusted nodes in your E-Business Suite
With 11.5.10 and higher you need to add the 10 G application server mode as a trusted node withing your E-Business suite You can do this through your Oracle Applications Manager Oracle Applications Manager=>Applications Dashboard=>Security=>Manage Security Options. You need to run autoconfig after this and bounce your database listener.
Restart your HTTP listener.
Restart your Apache HTTP listener to have your SSO registration take effect.
You may need to apply additional patches based on the E-Business Suite products installed.
ABSENCE OF mod_plsql IN R12
Running APEX with Oracle Applications Release 12 will not be that straightforward after all. The reason being the absence of mod_plsql in the Release 12 Application Server. In this post i will explore this topic a bit further and understand what exactly does the mod_plsql do and its absence in Oracle Applications Release 12.
mod_plsql
mod_plsql is a extension module of the Apache Web Server which is the core component of the Oracle Application server. It was also formally referred to as Oracle PLSQL Cartridge. The main function of the mod_plsql is that is allows the middle tier or the web server to understand and execute plsql code. This is particular useful in generation of dynamic web pages. The mod_plsql makes a connection to your database based on the information defined by your Data Access Descriptor (DAD) settings. That is in Oracle Applications the wdbsrv.app file would be used by the mod_plsql to connect to your database and execute the sql/plsql code against it. What this does mean is that virtually almost any plsql code can be executed through the web browser via a http/https protocol.
In a default apache web server configuration mod_plsql is configured and started by default.The Oracle Application server both standalone and the one bundled within Oracle Applications Release 11i.
mod_plsql Vulnerabilities
Although i am yet to see any official document from Oracle on the mod_plsql's demise in release 12 apart from Steven Chan’s blog and the Oracle Open World presentations, the reason for its exclusion are not mentioned.
The main reason which i feel is the security vulnerabilities that mod_plsql has. Since a connection to a database is possible relatively easily in a mod_plsql implementation its gives rise to security threats. In fact it allows anyone with access to the Oracle Application web server to execute any sql /plsql code against the APPS schema and view any data which is visible to the APPS user. This obviously quite dangerous. Also exists a risk of sql injection, which is one of the most commonly used techniques by hackers. Sql injection is a technique where the hacker tries to add in malicious code in between a valid sql/plsql code.This often makes the system quite vulnerable and difficult to detect the intrusion.
Although there have been workaround to block the mod_plsql vulnerabilities, they have been known to cause problems in complex implementations of Oracle Applications. These vulnerabilities have not gone unnoticed by oracle and it has relase Oracle Security Alert #28 which takes about the risk arising from the mod_plsql.
As a result i feel the security vulnerabilities surrounding mod_plsql would have been one of the major factors for Oracle to decide to de support mod_plsql in Oracle Applications Release 12.
Oracle Applications Framework.
When i has started blogging my third post covered Oracle Applications Framework(OAF).Its time to revisit the topic now. The Oracle Applications Framework is a java framework which is based on the J2EE MVC design pattern and allows to execute HTMl,XML,PL/SQL,Java and web services without compromising on security. The connection to the database in Oracle Applications Framework model is done through Java Database Connection (JDBC) Drivers.
The Oracle Applications Framework comes bundled in a default installation of Oracle Applications Release 11.5.10 and later for Oracle Applications Release 11.5.9 and prior you would be required to upgrade to the latest AD patchset level to be able to use Oracle Applications Framework. For the current release of OAF you must have be on java 1.3 atleast. The actual requirements for OAF in Release 12 are not known as the official documentation on that is yet to be released.
Apart from addressing the security vulnerabilities OAF also allows the out of box customizations of the Oracle Applications imodules. In Oracle Applications Release 12 all customizations which use the application server mod_plsql would have to be migrated to the Oracle Applications Framework model.
Additional References
Red-database-security.com's Sql Injection via mod_plsql
Steven Chan's Post on Release 12 Tech Stack
mod_plsql
mod_plsql is a extension module of the Apache Web Server which is the core component of the Oracle Application server. It was also formally referred to as Oracle PLSQL Cartridge. The main function of the mod_plsql is that is allows the middle tier or the web server to understand and execute plsql code. This is particular useful in generation of dynamic web pages. The mod_plsql makes a connection to your database based on the information defined by your Data Access Descriptor (DAD) settings. That is in Oracle Applications the wdbsrv.app file would be used by the mod_plsql to connect to your database and execute the sql/plsql code against it. What this does mean is that virtually almost any plsql code can be executed through the web browser via a http/https protocol.
In a default apache web server configuration mod_plsql is configured and started by default.The Oracle Application server both standalone and the one bundled within Oracle Applications Release 11i.
mod_plsql Vulnerabilities
Although i am yet to see any official document from Oracle on the mod_plsql's demise in release 12 apart from Steven Chan’s blog and the Oracle Open World presentations, the reason for its exclusion are not mentioned.
The main reason which i feel is the security vulnerabilities that mod_plsql has. Since a connection to a database is possible relatively easily in a mod_plsql implementation its gives rise to security threats. In fact it allows anyone with access to the Oracle Application web server to execute any sql /plsql code against the APPS schema and view any data which is visible to the APPS user. This obviously quite dangerous. Also exists a risk of sql injection, which is one of the most commonly used techniques by hackers. Sql injection is a technique where the hacker tries to add in malicious code in between a valid sql/plsql code.This often makes the system quite vulnerable and difficult to detect the intrusion.
Although there have been workaround to block the mod_plsql vulnerabilities, they have been known to cause problems in complex implementations of Oracle Applications. These vulnerabilities have not gone unnoticed by oracle and it has relase Oracle Security Alert #28 which takes about the risk arising from the mod_plsql.
As a result i feel the security vulnerabilities surrounding mod_plsql would have been one of the major factors for Oracle to decide to de support mod_plsql in Oracle Applications Release 12.
Oracle Applications Framework.
When i has started blogging my third post covered Oracle Applications Framework(OAF).Its time to revisit the topic now. The Oracle Applications Framework is a java framework which is based on the J2EE MVC design pattern and allows to execute HTMl,XML,PL/SQL,Java and web services without compromising on security. The connection to the database in Oracle Applications Framework model is done through Java Database Connection (JDBC) Drivers.
The Oracle Applications Framework comes bundled in a default installation of Oracle Applications Release 11.5.10 and later for Oracle Applications Release 11.5.9 and prior you would be required to upgrade to the latest AD patchset level to be able to use Oracle Applications Framework. For the current release of OAF you must have be on java 1.3 atleast. The actual requirements for OAF in Release 12 are not known as the official documentation on that is yet to be released.
Apart from addressing the security vulnerabilities OAF also allows the out of box customizations of the Oracle Applications imodules. In Oracle Applications Release 12 all customizations which use the application server mod_plsql would have to be migrated to the Oracle Applications Framework model.
Additional References
Red-database-security.com's Sql Injection via mod_plsql
Steven Chan's Post on Release 12 Tech Stack
Linux BASICS
Linux How-To
Although i have been working with Oracle Application all various Unix flavors my favorite one has been Linux. In today's post i will shift focus from Oracle Applications and discuss some tips for doing some frequently used tasks on the Operating System.
This post is my first in a series of posts which i intend to put up here on the operating system. Although most of you would be using these quite frequently I just though of putting them in one place.
Finding Your Linux Release
The first set you would require to do most of the times as an Applications DBA before you start installing or troubleshooting is to find out the version of Linux you are running.
This you can get from a static file redhat-release located in the /etc directory
view /etc/redhat-release
Red Hat Enterprise Linux AS release 4 (Nahant Update 2)
NFS mounting on Linux
Most often it is required to do a NFS mount of your disks across different servers. This particularly useful for doing Applications Installations and Patching. There are two aspects of configuration involved here. One is the sever that is the which is sharing the file system and the other is client which the host that is mounting the shared file system.
Supposing you want to mount a u01/sam on Node_A to Node_B
Configurations on Node_A
edit the /etc/exports file
vi /etc/exports
add the filesystem to mount
/u01/sam ro Node_B
you can either use the option ro which means read only or in case you wish to allow node_b to write into the filesystem use the rw option which is read writeable.
The change in exports file takes effect only after the restart of your NFS service daemon. use the service command to do that.
# service nfs restart
Shutting down NFS mountd: [ OK ]
Shutting down NFS daemon: [ OK ]
Shutting down NFS quotas: [ OK ]
Shutting down NFS services: [ OK ]
Starting NFS services: [ OK ]
Starting NFS quotas: [ OK ]
Starting NFS daemon: [ OK ]
Starting NFS mountd: [ OK ]
Configuration for Node_B
On Node_B simply create the mount point to hold the shared file system and mount it using the mount command.
#mkdir sam
#mount -t nfs Node_A:/u01/sam /sam
Setting Kernel Parameters
Most oracle products require certain kernel parameters to be set as a pre requisite for installation. Common kernel parameters include parameters for shared memory .
The /etc/sysctl.conf file takes care of your kernel parameters.
#vi /etc/sysctl.conf
kernel.shmmax = 2147483648
kernel.shmmni = 128
kernel.shmall = 2097152
kernel.sem = 250 32000 100 128
fs.file-max = 65536
net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 1024 65000
However changes made to this file take effect only after the next reboot.
The sysctl command can be used to set the kernel parameter at runtime in linux.
sysctl -w kernel.shmmax=2147483648
You must however make the change in the /etc/sysctl.conf so that it is permanent.
Increasing the Swap space at runtime
Imagine this, you start the OUI and your pre installation check fails due to insufficient swap space. Now I agree that you got to check all this before starting the installation but just in case you missed it. You could always increase it on the fly.
Check the memory on your server
# free -m
total used free shared buffers cached
Mem: 8117 3204 4913 0 77 2648
-/+ buffers/cache: 478 7639
Swap: 101 0 101
Now say you need to increase it by 500 MB for your server, first locate a place you can spare this 500 MB in my case i found it in /u01
Use the dd command to create a swapfile
#cd /u01
# dd if=/dev/zero of=swapfile bs=1024 count=512000
512000+0 records in
512000+0 records out
# ls -ltr
drwx------ 2 root root 16384 May 1 2006 lost+found
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 524288000 Nov 28 13:58 swapfile
Next issue the following two commands
# mkswap swapfile
Setting up swapspace version 1, size = 524283 kB
# swapon swapfile
Now check you memory again
# free -m
total used free shared buffers cached
Mem: 8117 2176 5941 0 45 1975
-/+ buffers/cache: 155 7962
Swap: 601 0 601
Bingo! here is your increased SWAP.
To make this change permanent add the line in your etc/fstab
/u01/swapfile swap swap defaults 0 0
Although i have been working with Oracle Application all various Unix flavors my favorite one has been Linux. In today's post i will shift focus from Oracle Applications and discuss some tips for doing some frequently used tasks on the Operating System.
This post is my first in a series of posts which i intend to put up here on the operating system. Although most of you would be using these quite frequently I just though of putting them in one place.
Finding Your Linux Release
The first set you would require to do most of the times as an Applications DBA before you start installing or troubleshooting is to find out the version of Linux you are running.
This you can get from a static file redhat-release located in the /etc directory
view /etc/redhat-release
Red Hat Enterprise Linux AS release 4 (Nahant Update 2)
NFS mounting on Linux
Most often it is required to do a NFS mount of your disks across different servers. This particularly useful for doing Applications Installations and Patching. There are two aspects of configuration involved here. One is the sever that is the which is sharing the file system and the other is client which the host that is mounting the shared file system.
Supposing you want to mount a u01/sam on Node_A to Node_B
Configurations on Node_A
edit the /etc/exports file
vi /etc/exports
add the filesystem to mount
/u01/sam ro Node_B
you can either use the option ro which means read only or in case you wish to allow node_b to write into the filesystem use the rw option which is read writeable.
The change in exports file takes effect only after the restart of your NFS service daemon. use the service command to do that.
# service nfs restart
Shutting down NFS mountd: [ OK ]
Shutting down NFS daemon: [ OK ]
Shutting down NFS quotas: [ OK ]
Shutting down NFS services: [ OK ]
Starting NFS services: [ OK ]
Starting NFS quotas: [ OK ]
Starting NFS daemon: [ OK ]
Starting NFS mountd: [ OK ]
Configuration for Node_B
On Node_B simply create the mount point to hold the shared file system and mount it using the mount command.
#mkdir sam
#mount -t nfs Node_A:/u01/sam /sam
Setting Kernel Parameters
Most oracle products require certain kernel parameters to be set as a pre requisite for installation. Common kernel parameters include parameters for shared memory .
The /etc/sysctl.conf file takes care of your kernel parameters.
#vi /etc/sysctl.conf
kernel.shmmax = 2147483648
kernel.shmmni = 128
kernel.shmall = 2097152
kernel.sem = 250 32000 100 128
fs.file-max = 65536
net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 1024 65000
However changes made to this file take effect only after the next reboot.
The sysctl command can be used to set the kernel parameter at runtime in linux.
sysctl -w kernel.shmmax=2147483648
You must however make the change in the /etc/sysctl.conf so that it is permanent.
Increasing the Swap space at runtime
Imagine this, you start the OUI and your pre installation check fails due to insufficient swap space. Now I agree that you got to check all this before starting the installation but just in case you missed it. You could always increase it on the fly.
Check the memory on your server
# free -m
total used free shared buffers cached
Mem: 8117 3204 4913 0 77 2648
-/+ buffers/cache: 478 7639
Swap: 101 0 101
Now say you need to increase it by 500 MB for your server, first locate a place you can spare this 500 MB in my case i found it in /u01
Use the dd command to create a swapfile
#cd /u01
# dd if=/dev/zero of=swapfile bs=1024 count=512000
512000+0 records in
512000+0 records out
# ls -ltr
drwx------ 2 root root 16384 May 1 2006 lost+found
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 524288000 Nov 28 13:58 swapfile
Next issue the following two commands
# mkswap swapfile
Setting up swapspace version 1, size = 524283 kB
# swapon swapfile
Now check you memory again
# free -m
total used free shared buffers cached
Mem: 8117 2176 5941 0 45 1975
-/+ buffers/cache: 155 7962
Swap: 601 0 601
Bingo! here is your increased SWAP.
To make this change permanent add the line in your etc/fstab
/u01/swapfile swap swap defaults 0 0
Adding an Additional Node to an existing Oracle Applications Instance.
Adding an Additional Node to an existing Oracle Applications Instance.
Coming to the advanced configurations in ebusiness suite, today my current post will talk about introducing a new node to an already existing ebusiness suite.
Current configuration
A single node instance of 11.5.10.2 on Linux This is referred as Node A in the rest of the post.
Task
Plan to introduce a new Linux node (referred as Node B) for the web and the forms server and split the instance into a two node configuration.
Node A Configuration
Application User: applsam
Home Dir: /u02/sam/applsam
Oracle User: orasam
Home Dir: /u02/sam/orasam
Instance SID: SAM
The task can be accomplished either by implementing a SHARED APPL_TOP concept or by using rapidclone. I am using rapidclone in my current post here.
The brief outline of steps to be performed to accomplish this task are.
* Running Pre Clone on Node A.
* Copying the Application Tier Files to Node B.
* Running Post Clone on Node A DB Tier and Apps Tier.
* Running post clone on Node B Apps Tier.
* Adding the additional node script on Node A.
Running Rapid Clone on Node A Database Tier and Applications Tier.
Pre-Clone on database Tier Of Node A
Login to Node A as the database owner and set the environment
# su - orasam
$ cd samdb
$ cd 9.2.0/
$ . ./Sam_Node_A.env
$cd $ORACLE_HOME/appsutil/scripts/Sam
$ perl adpreclone.pl dbTier
Pre-clone on Node A application tier
Login to to Node A which is also our source system as the applications user and set the environment.
# su - applsam
$ cd samappl
$ . ./APPSORA.env
$ cd $COMMON_TOP/admin/scripts/sam
$ perl adpreclone.pl appsTier
Disable security option
In Oracle Applications 11.5.10 the SQL*NET restricted security option is enabled by default. As a result your new node Node_B will not be able to connect to the database. You must either disable this security option or the better way is to add Node_B is the list of trusted nodes through OAM.
Oracle Applications Manager -> Security ->Disable Restricted Sectrity Option.
After this you must run Autoconfig on the database Tier and restart your listener.
# su - orasam
$ cd $ORACLE_HOME/appsutil/scripts/SAM_NOde_A
$ ./adautocfg.sh
Restart your listener.
$ ./addlnctl.sh stop sam
$ ./addlnctl.sh start sam
Preparing the new node (Node B) to copy the application tier file system.
On Node B make the following dir structure
# cd /u02
# mkdir sam
# chmod -R 777 sam
Copy the files across to Node B
Shutdown on Application and Database services on Node A
tar -cf - applsam | ssh Node_B tar -xf - -C /u02/sam/
Post Clone on Node A Database Tier
Now you must run your post clone (adcfgclone.pl) on the database tier of Node A preserving the original values
# su - orasam
$ cd samdb/9.2.0/appsutil/clone/bin
$ perl adcfgclone.pl dbTier
Post Clone on Node A Applications Tier
Now you run your post clone (adcfgclone.pl) on Node A applications Tier. you must remember to configure the services you require on tiis node in our case the CM and the Admin Node.
$ perl adcfgclone.pl appsTier
Once completed sucessfully this will start the specified services only in our source Node Node A.
Running Post clone On Node B
Next you run your post clone on the Node B again specifying the services you like to configure which in our case were forms server and the web server.
$ perl adcfgclone.pl appsTier
Execute the Add Node script on Node A
After sourcing your environment file you must run the adaddnode.pl script on node A
#su - applsam
$ cd $COMMON_TOP/clone/bin
$ perl adaddnode.pl
The script will promt you for your APPS user and password and do the required new node entries to the database FND tables.
You can check the details of this new node and status through Oracle Applications Manager.
References.
Advanced Configurations and Topologies for Enterprise Deployments of E-Business Suite 11i Note Id 217368.1
Cloning Oracle Applications Release 11i with Rapid Clone Note Id 230672.1
Coming to the advanced configurations in ebusiness suite, today my current post will talk about introducing a new node to an already existing ebusiness suite.
Current configuration
A single node instance of 11.5.10.2 on Linux This is referred as Node A in the rest of the post.
Task
Plan to introduce a new Linux node (referred as Node B) for the web and the forms server and split the instance into a two node configuration.
Node A Configuration
Application User: applsam
Home Dir: /u02/sam/applsam
Oracle User: orasam
Home Dir: /u02/sam/orasam
Instance SID: SAM
The task can be accomplished either by implementing a SHARED APPL_TOP concept or by using rapidclone. I am using rapidclone in my current post here.
The brief outline of steps to be performed to accomplish this task are.
* Running Pre Clone on Node A.
* Copying the Application Tier Files to Node B.
* Running Post Clone on Node A DB Tier and Apps Tier.
* Running post clone on Node B Apps Tier.
* Adding the additional node script on Node A.
Running Rapid Clone on Node A Database Tier and Applications Tier.
Pre-Clone on database Tier Of Node A
Login to Node A as the database owner and set the environment
# su - orasam
$ cd samdb
$ cd 9.2.0/
$ . ./Sam_Node_A.env
$cd $ORACLE_HOME/appsutil/scripts/Sam
$ perl adpreclone.pl dbTier
Pre-clone on Node A application tier
Login to to Node A which is also our source system as the applications user and set the environment.
# su - applsam
$ cd samappl
$ . ./APPSORA.env
$ cd $COMMON_TOP/admin/scripts/sam
$ perl adpreclone.pl appsTier
Disable security option
In Oracle Applications 11.5.10 the SQL*NET restricted security option is enabled by default. As a result your new node Node_B will not be able to connect to the database. You must either disable this security option or the better way is to add Node_B is the list of trusted nodes through OAM.
Oracle Applications Manager -> Security ->Disable Restricted Sectrity Option.
After this you must run Autoconfig on the database Tier and restart your listener.
# su - orasam
$ cd $ORACLE_HOME/appsutil/scripts/SAM_NOde_A
$ ./adautocfg.sh
Restart your listener.
$ ./addlnctl.sh stop sam
$ ./addlnctl.sh start sam
Preparing the new node (Node B) to copy the application tier file system.
On Node B make the following dir structure
# cd /u02
# mkdir sam
# chmod -R 777 sam
Copy the files across to Node B
Shutdown on Application and Database services on Node A
tar -cf - applsam | ssh Node_B tar -xf - -C /u02/sam/
Post Clone on Node A Database Tier
Now you must run your post clone (adcfgclone.pl) on the database tier of Node A preserving the original values
# su - orasam
$ cd samdb/9.2.0/appsutil/clone/bin
$ perl adcfgclone.pl dbTier
Post Clone on Node A Applications Tier
Now you run your post clone (adcfgclone.pl) on Node A applications Tier. you must remember to configure the services you require on tiis node in our case the CM and the Admin Node.
$ perl adcfgclone.pl appsTier
Once completed sucessfully this will start the specified services only in our source Node Node A.
Running Post clone On Node B
Next you run your post clone on the Node B again specifying the services you like to configure which in our case were forms server and the web server.
$ perl adcfgclone.pl appsTier
Execute the Add Node script on Node A
After sourcing your environment file you must run the adaddnode.pl script on node A
#su - applsam
$ cd $COMMON_TOP/clone/bin
$ perl adaddnode.pl
The script will promt you for your APPS user and password and do the required new node entries to the database FND tables.
You can check the details of this new node and status through Oracle Applications Manager.
References.
Advanced Configurations and Topologies for Enterprise Deployments of E-Business Suite 11i Note Id 217368.1
Cloning Oracle Applications Release 11i with Rapid Clone Note Id 230672.1
Installing 10G Application Server
Installing 10G Application Server
Last week i spent a considerable amount of time working on Oracle Application server configurations, i also revisited some of the installation of the core application server components. For starters i will blog with about the installation of Oracle Applications server.
The Oracle Application Server is divided into two main server side components which are infrastructure and middle tier. Apart from there it also includes developer kits.
These components can be installed on the same server but must have separate ORACLE_HOMEs. Also the infrastructure must be installed first after which you must install your middle tier components as the meta data repository is a part of the infrastructure installation.
Another important fact to note is that the oracle application server uses 1521 port as default for its listener. In case the port is used by another listener on your system you must share it with this instance or you must manually configure the application server DB listener to use a different port.
The OS is Redhat Linux AS
The Version Of Oracle Application Server is 10.1.2.0
1.Required OS packages
The first step would be to make sure you have the following packages (or a higher version) installed
glibc-2.3.4-2.9
glibc-common-2.3.4-2.9
binutils-2.15.92.0.2-13
compat-libstdc++-296-2.96-132.7.2
gcc-3.4.3-22.1
gcc-c++-3.4.3-22.1
libstdc++-3.4.3-22.1
libstdc++-devel-3.4.3-22.1
openmotif21-2.1.30-11.RHEL4.4
pdksh-5.2.14-30
setarch-1.6-1
make-3.80-5
gnome-libs-1.4.1.2.90-44.1
sysstat-5.0.5-1
compat-db-4.1.25-9
control-center-2.8.0-12
xscreensaver-4.18-5.rhel4.2
For Linux you can use the rpm -qa|grep command to check.
2. OS Directories
Next we will make a directory structure to hold your application server components.
# cd /u03
# mkdir oracleAS
# chmod -R 777 oracleAS
3. OS User Accounts
Having two seperate OS accounts for the infrastructure and middle tier comapnets make it easier to manage the installation.
# useradd -g dba -d /u03/oracleAS/asinf asinf
# useradd -g dba -d /u03/oracleAS/asmid asmid
4.Oracle Inventory
Make sure to set your oracle inventory location to a accessible location.
vi /etc/oraInst.loc
inventory_loc=/u03/oracleAS/oraInventory
inst_group=dba
5. Starting the installation.
The installation has to be started as the infrastructure user (asinf), but executing the runInstaller
executable. The first screen is the welcome screen.
6.In this screen you would specify your ORACLE_HOME for your infrastructure.
7. The next screen presents you with the option of installing either of the application server
componets as bloged above we will proceed with the installation of the infrastructure first.
8.The next screen you can choose to install the Oracle Internet Directory, Single Sign On and Meta Data Repository, you could choose to make either of them or all of them included in your application server infrastructure.
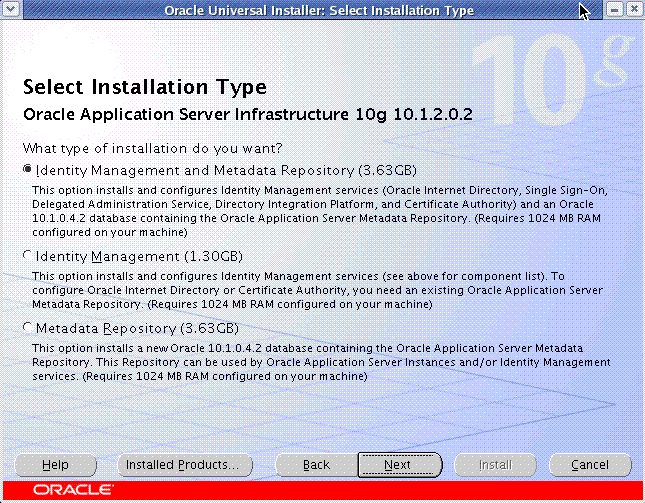
9.Next the installer will carry out a pre installation check of your OS.
10. You must conform pre requisite as root privileges on your system.
11. This screen will allow you to choose the services which the installer will configure and start for
you.
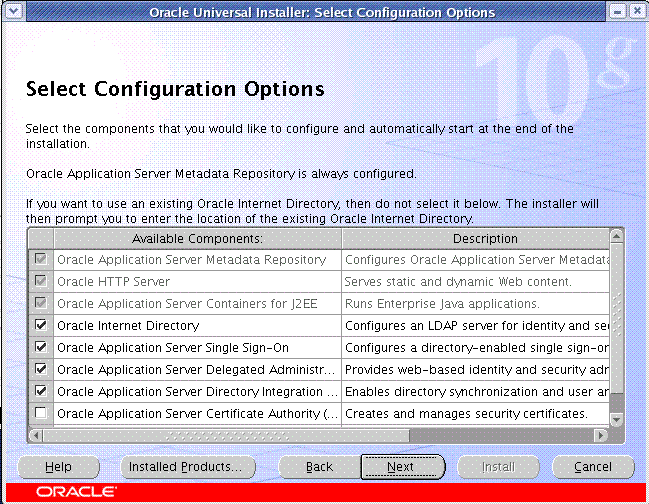
12. In this screen you can choose either to let the installer decide the ports for the various 10G
Application server services or you can prove one manually using the static port file.
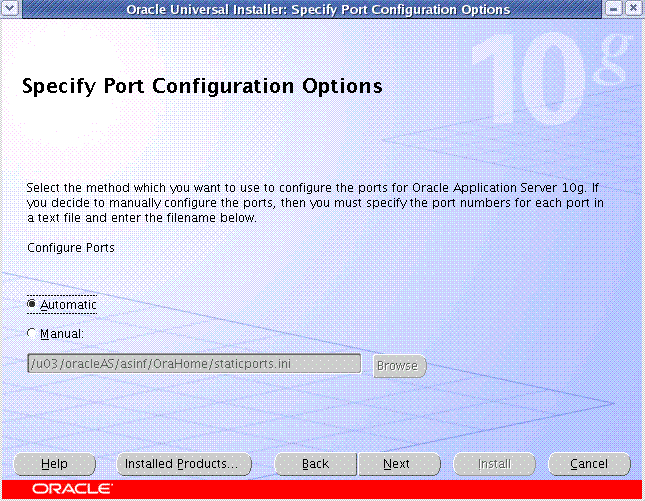
13. This screen will display the default realm for your OID
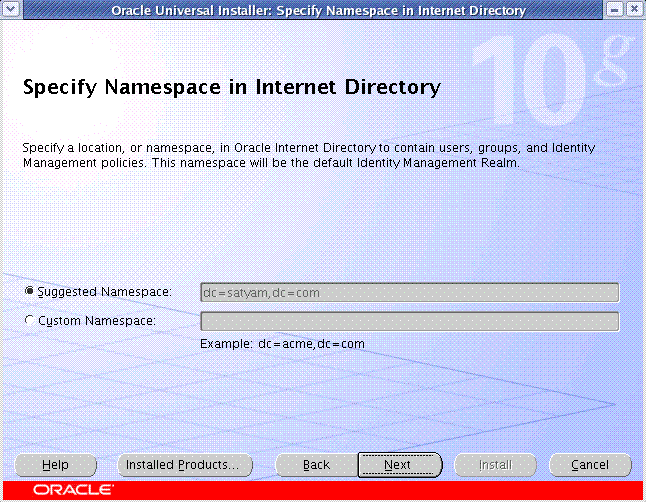
14. Here you can choose your database SID and also the location for your datafile locations.
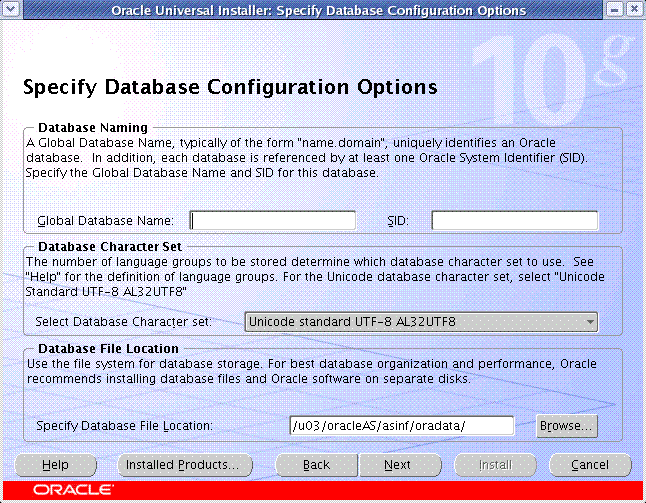
15.Next you specify the passwords for your database schema (Unfortunately it does not allow you to specify passwords for the PORTAL schema ;)
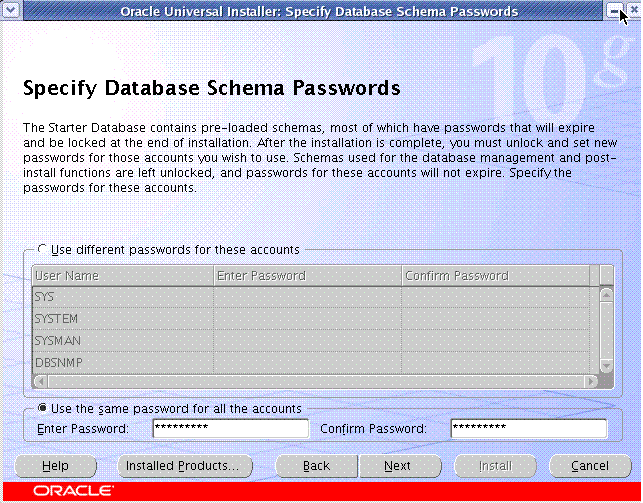
16. In this screen you specify the your instance name and the ias_admin password.
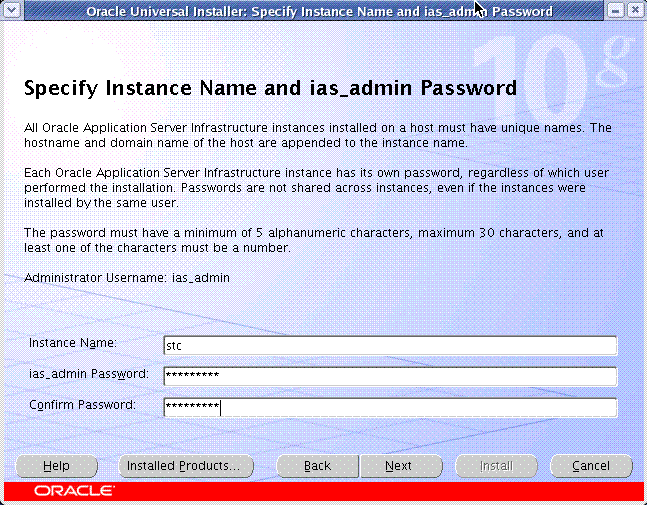
17. The next screen will display the components the installer will install.
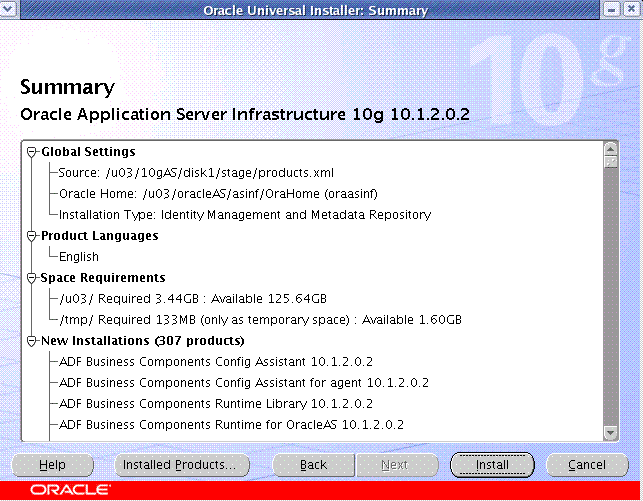
18. After this a progress bar displays the status of the installation, allowing you just enough time to catch up on your mails.
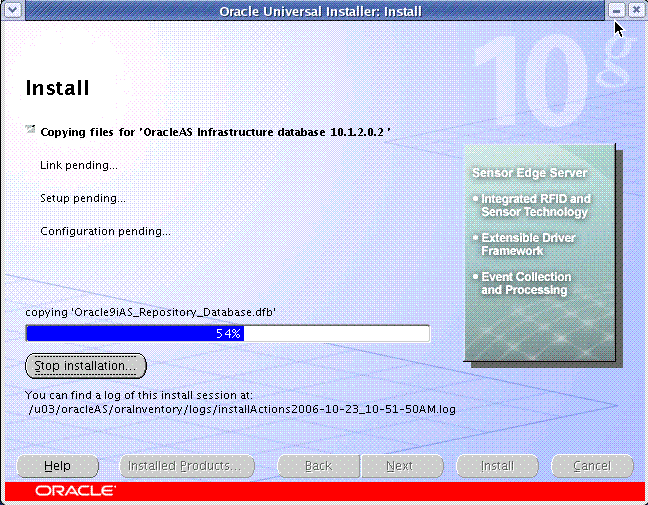
19.As a post installation step the installer configures and starts up the installed products.
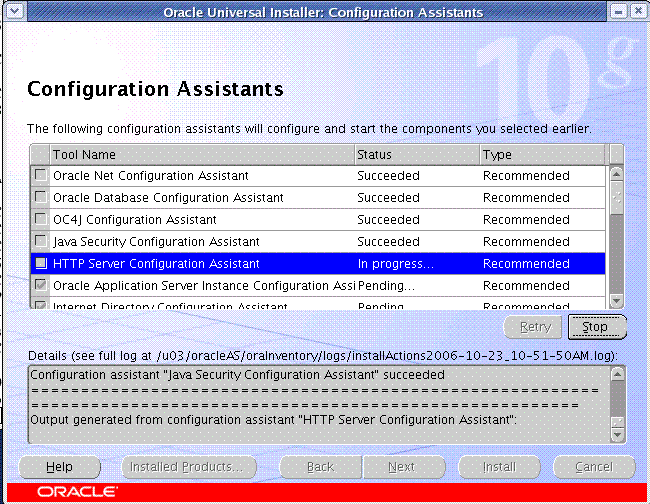
20.You now can start with the installation of the middle tier component as the asmid OS user and choose to install the middle tier services like portal.
21. The other steps are all repetitive except the screen where you have register your middle tier component with your OID which was installed as part of your infrastructure.
There two important files that the installation process creates, the first is the portlist.ini located at the $ORACLE_HOME/install directory this file contains the various port numbers used by the application server services. The other file is the supportinfo.txt which contains the URLs to access the installation.
Last week i spent a considerable amount of time working on Oracle Application server configurations, i also revisited some of the installation of the core application server components. For starters i will blog with about the installation of Oracle Applications server.
The Oracle Application Server is divided into two main server side components which are infrastructure and middle tier. Apart from there it also includes developer kits.
These components can be installed on the same server but must have separate ORACLE_HOMEs. Also the infrastructure must be installed first after which you must install your middle tier components as the meta data repository is a part of the infrastructure installation.
Another important fact to note is that the oracle application server uses 1521 port as default for its listener. In case the port is used by another listener on your system you must share it with this instance or you must manually configure the application server DB listener to use a different port.
The OS is Redhat Linux AS
The Version Of Oracle Application Server is 10.1.2.0
1.Required OS packages
The first step would be to make sure you have the following packages (or a higher version) installed
glibc-2.3.4-2.9
glibc-common-2.3.4-2.9
binutils-2.15.92.0.2-13
compat-libstdc++-296-2.96-132.7.2
gcc-3.4.3-22.1
gcc-c++-3.4.3-22.1
libstdc++-3.4.3-22.1
libstdc++-devel-3.4.3-22.1
openmotif21-2.1.30-11.RHEL4.4
pdksh-5.2.14-30
setarch-1.6-1
make-3.80-5
gnome-libs-1.4.1.2.90-44.1
sysstat-5.0.5-1
compat-db-4.1.25-9
control-center-2.8.0-12
xscreensaver-4.18-5.rhel4.2
For Linux you can use the rpm -qa|grep
2. OS Directories
Next we will make a directory structure to hold your application server components.
# cd /u03
# mkdir oracleAS
# chmod -R 777 oracleAS
3. OS User Accounts
Having two seperate OS accounts for the infrastructure and middle tier comapnets make it easier to manage the installation.
# useradd -g dba -d /u03/oracleAS/asinf asinf
# useradd -g dba -d /u03/oracleAS/asmid asmid
4.Oracle Inventory
Make sure to set your oracle inventory location to a accessible location.
vi /etc/oraInst.loc
inventory_loc=/u03/oracleAS/oraInventory
inst_group=dba
5. Starting the installation.
The installation has to be started as the infrastructure user (asinf), but executing the runInstaller
executable. The first screen is the welcome screen.
6.In this screen you would specify your ORACLE_HOME for your infrastructure.
7. The next screen presents you with the option of installing either of the application server
componets as bloged above we will proceed with the installation of the infrastructure first.
8.The next screen you can choose to install the Oracle Internet Directory, Single Sign On and Meta Data Repository, you could choose to make either of them or all of them included in your application server infrastructure.
9.Next the installer will carry out a pre installation check of your OS.
10. You must conform pre requisite as root privileges on your system.
11. This screen will allow you to choose the services which the installer will configure and start for
you.
12. In this screen you can choose either to let the installer decide the ports for the various 10G
Application server services or you can prove one manually using the static port file.
13. This screen will display the default realm for your OID
14. Here you can choose your database SID and also the location for your datafile locations.
15.Next you specify the passwords for your database schema (Unfortunately it does not allow you to specify passwords for the PORTAL schema ;)
16. In this screen you specify the your instance name and the ias_admin password.
17. The next screen will display the components the installer will install.
18. After this a progress bar displays the status of the installation, allowing you just enough time to catch up on your mails.
19.As a post installation step the installer configures and starts up the installed products.
20.You now can start with the installation of the middle tier component as the asmid OS user and choose to install the middle tier services like portal.
21. The other steps are all repetitive except the screen where you have register your middle tier component with your OID which was installed as part of your infrastructure.
There two important files that the installation process creates, the first is the portlist.ini located at the $ORACLE_HOME/install directory this file contains the various port numbers used by the application server services. The other file is the supportinfo.txt which contains the URLs to access the installation.
Changing the Net Listener Port in Oracle Applications Server 10g
Changing the Net Listener Port in Oracle Applications Server 10g
In my previous post I discussed installing the 10g application server. The Application server installation uses the port 1521 as the default port for the application meta data repository. If you already have a listener using that port you have the option of either sharing the listener or configuring a new listener. In my case i tried to change the listener and found out it included just a little bit more than just changing the listener.ora file.
I am listing out the steps that i performed to configure a new listener and get the applications server back to shape.
System Overview
10g Application server with infrastructure and middle tier installed on the same box.
Infrastructure Tier Services
OID
HTTP Server
Middle Tier Application
Portal
OS Users
Infrastructure OS user: asinf
Middle Tier OS user: asmid
Task
Current Listener running on port 1521.
Configuring a new listener on port 1525
Shutdown Services.
Shutdown all the infrastructure and middle tier services.
su - asmid
$opmnctl stopall
$emctl stop iasconsole
su - asinf
$opmnctl stopall
$emctl stop iasconsole
Shutdown Your Infrastructure Listener
# su - asinf
$lsnrctl stop
Change The Listener Configuration
Make the change to have the new post number in the lsitener.ora file on your infrastructure tier.
# su - asinf
$cd $ORACLE_HOME/network/admin
$vi listener.ora
SID_LIST_SAM =
(SID_LIST =
(SID_DESC =
(SID_NAME = PLSExtProc)
(ORACLE_HOME = /u03/oracleAS/asinf/OraHome)
(PROGRAM = extproc)
)
)
SAM =
(DESCRIPTION_LIST =
(DESCRIPTION =
(ADDRESS_LIST =
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST =
samlnx02.appsdbablog.com)(PORT = 1525))
)
(ADDRESS_LIST =
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = IPC)(KEY = EXTPROC))
)
)
)
Change Your TNSNAMES
After this you need to make the change reflecting the new port in your TNSNAMES.ora file on both the infrastructure tier and the middle tier.
$su - asinf
$ vi $ORACLE_HOME/network/admin/tnsnames.ora
EXTPROC_CONNECTION_DATA =
(DESCRIPTION =
(ADDRESS_LIST =
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = samlnx02.appsdbablog.com)(PORT
= 1525))
)
(CONNECT_DATA =
(SERVICE_NAME = PLSExtProc)
)
)
SAM =
(DESCRIPTION =
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = samlnx02.appsdbablog.com)(PORT =
1525))
(CONNECT_DATA =
(SERVER = DEDICATED)
(SERVICE_NAME = sam.appsdbablog.com)
)
)
Also replicate this change in middle tier tnsnames.ora.
Start Your Listener
Start your infrastructure tier listener.
# su - asinf
$lsnrctl start SAM
Set The New Listener At The Database Level.
You must execute this command in your infrastructure database to have the parameter local_listener set to your new listener.
# su - asinf
$sqlplus "/ as sysdba"
SQL*Plus: Release 10.1.0.4.2 - Production on Thu Oct 26 18:38:38 2006
Copyright (c) 1982, 2005, Oracle. All rights reserved.
Connected to:
Oracle Database 10g Enterprise Edition Release 10.1.0.4.2 - Production
With the Partitioning, OLAP and Data Mining options
SQL> alter system set local_listener='SAM';
system altered
Bounce The Database.
Stop and startup your meta data repository database to have it register the new listener name.
Start Your OID On The Infrastructure Tier
# su - asinf
$opmnctl startproc ias-component=OID
Change The Port Number In OID.
Start the Oracle Directory Manager from your desktop if you have the client installed else you can use the one on the server at $ORACLE_HOME/bin/oidadmin
Under Entry Management->cn=Oracle Context->cn=SAM->orclnetdescstring chnage the value of the new port here.
Change The Other Config Files.
Based on your installation you may need to change the following files also
$ORACLE_HOME/sysman/emd/targets.xml
$ORACLE_HOME/Apache/modplsql/conf/dads.conf

In my previous post I discussed installing the 10g application server. The Application server installation uses the port 1521 as the default port for the application meta data repository. If you already have a listener using that port you have the option of either sharing the listener or configuring a new listener. In my case i tried to change the listener and found out it included just a little bit more than just changing the listener.ora file.
I am listing out the steps that i performed to configure a new listener and get the applications server back to shape.
System Overview
10g Application server with infrastructure and middle tier installed on the same box.
Infrastructure Tier Services
OID
HTTP Server
Middle Tier Application
Portal
OS Users
Infrastructure OS user: asinf
Middle Tier OS user: asmid
Task
Current Listener running on port 1521.
Configuring a new listener on port 1525
Shutdown Services.
Shutdown all the infrastructure and middle tier services.
su - asmid
$opmnctl stopall
$emctl stop iasconsole
su - asinf
$opmnctl stopall
$emctl stop iasconsole
Shutdown Your Infrastructure Listener
# su - asinf
$lsnrctl stop
Change The Listener Configuration
Make the change to have the new post number in the lsitener.ora file on your infrastructure tier.
# su - asinf
$cd $ORACLE_HOME/network/admin
$vi listener.ora
SID_LIST_SAM =
(SID_LIST =
(SID_DESC =
(SID_NAME = PLSExtProc)
(ORACLE_HOME = /u03/oracleAS/asinf/OraHome)
(PROGRAM = extproc)
)
)
SAM =
(DESCRIPTION_LIST =
(DESCRIPTION =
(ADDRESS_LIST =
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST =
samlnx02.appsdbablog.com)(PORT = 1525))
)
(ADDRESS_LIST =
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = IPC)(KEY = EXTPROC))
)
)
)
Change Your TNSNAMES
After this you need to make the change reflecting the new port in your TNSNAMES.ora file on both the infrastructure tier and the middle tier.
$su - asinf
$ vi $ORACLE_HOME/network/admin/tnsnames.ora
EXTPROC_CONNECTION_DATA =
(DESCRIPTION =
(ADDRESS_LIST =
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = samlnx02.appsdbablog.com)(PORT
= 1525))
)
(CONNECT_DATA =
(SERVICE_NAME = PLSExtProc)
)
)
SAM =
(DESCRIPTION =
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = samlnx02.appsdbablog.com)(PORT =
1525))
(CONNECT_DATA =
(SERVER = DEDICATED)
(SERVICE_NAME = sam.appsdbablog.com)
)
)
Also replicate this change in middle tier tnsnames.ora.
Start Your Listener
Start your infrastructure tier listener.
# su - asinf
$lsnrctl start SAM
Set The New Listener At The Database Level.
You must execute this command in your infrastructure database to have the parameter local_listener set to your new listener.
# su - asinf
$sqlplus "/ as sysdba"
SQL*Plus: Release 10.1.0.4.2 - Production on Thu Oct 26 18:38:38 2006
Copyright (c) 1982, 2005, Oracle. All rights reserved.
Connected to:
Oracle Database 10g Enterprise Edition Release 10.1.0.4.2 - Production
With the Partitioning, OLAP and Data Mining options
SQL> alter system set local_listener='SAM';
system altered
Bounce The Database.
Stop and startup your meta data repository database to have it register the new listener name.
Start Your OID On The Infrastructure Tier
# su - asinf
$opmnctl startproc ias-component=OID
Change The Port Number In OID.
Start the Oracle Directory Manager from your desktop if you have the client installed else you can use the one on the server at $ORACLE_HOME/bin/oidadmin
Under Entry Management->cn=Oracle Context->cn=SAM->orclnetdescstring chnage the value of the new port here.
Change The Other Config Files.
Based on your installation you may need to change the following files also
$ORACLE_HOME/sysman/emd/targets.xml
$ORACLE_HOME/Apache/modplsql/conf/dads.conf
Oracle Applications File System
Oracle Applications File System
A proper understanding of the file system that Oracle Applications implements is critical for efficiently working with and managing Oracle Applications.
The below discussion only a brief overview of the Applications file system and directory structures and does not include shared application tier file system.
The final structure your application file system takes depends upon the input parameters that you give while executing rapidinstall, it is carried across multiple nodes with the help of the config.txt which stores these parameters.
The [dbname] in this blog refer to your database name and generally the SID of your database which is also specified at the time of executing rapidinstall for installing oracle applications.
Since the installation start with the DB node first we will first talk about the DB Tier.
On the DB tier there two main top level directories which are [dbname]DATA and [dbname]DB.
The [dbname]DATA is also reffred as the DATA_TOP contains all the datafiles (.dbf) for the various tablespaces of your database. These include your System tablespace, Applications Tablespace, Temporary table Space etc. All the datafiles must reside within the DATA_TOP.It is however possible to have multiple DATA_TOPs within a Oracle Applications Instance, this is
particularly useful for spreading across your datafiles across multiple mount points or disks.
The second important top level directory of the database tier is [dbname]DB. This contains your 9i ORACLE_HOME (as in the case of 11.5.10).That is under this directory all the files need to run and maintain you database reside.any database upgrade like upgrading your applications database to 10g would involve upgrading this ORACLE_HOME.
Coming to the Applications Tier there are three important top level directories.
[dbname]APPL,[dbname]COMN and [dbname]ORA
The [dbname]APPL is also know as your APPL_TOP. The APPL_TOP contains the core technology files required for Oracle Applications it also contains individual subdirectories for all oracle applications products. For eg under the [dbname]APPL or the APPL_TOP you would find directories for AD,FND,GL etc. These product directories are also know as PRODUCT_TOPs like AD_TOP,GL_TOP etc. Each of the product directories have the sub directories like admin, driver, import, odf, sql, bin, forms,reports etc.
The second TOP level directory under the applications tier is the [dbname]COMN. This is also referred to as your COMMON_TOP.The COMMON_TOP contains files that are commonly used by different Oracle applications products as well as any third party applications that may have been integrated with Oracle applications.
The COMMON_TOP contains sub following sub directories.
admin which holds the place for concurrent manager log and out files in the log and out sub directories respectively. Also it contains a scripts subdirectory.
html which is also referred by the environment variable OA_HTML contains the HTML files, JSP,CSS and Java scripts that are used by Oracle Applications.
java subdirectory which holds the jar files, this is also referred to as the JAVA_TOP.
scripts subdirectory that contains the machine admin scripts like the adstpall.sh
util subdirectory contains third party utilities that are used in oracle applications like JRE from sun microsystems
Temp subdirectory used for caching
Portal subdirectory used to delivery rapid install portal pages.
The third top level directory under application tier is the [dbname]ORA directory.This contains the IAS ORACLE HOME and the 8.0.6 ORACLE HOME.
Apart from the Database ORACLE_HOME 11i uses two other ORACLE_HOMES.The first is the 8.0.6 ORACLE HOME.This is used for developer 6i products which are forms reports and graphics. The applications executables also link with the 8.0.6 libraries.
IAS ORACLE HOME is the ORACLE HOME used by the 9iAS application server which is the primary web server for Oracle Applications.
A proper understanding of the file system that Oracle Applications implements is critical for efficiently working with and managing Oracle Applications.
The below discussion only a brief overview of the Applications file system and directory structures and does not include shared application tier file system.
The final structure your application file system takes depends upon the input parameters that you give while executing rapidinstall, it is carried across multiple nodes with the help of the config.txt which stores these parameters.
The [dbname] in this blog refer to your database name and generally the SID of your database which is also specified at the time of executing rapidinstall for installing oracle applications.
Since the installation start with the DB node first we will first talk about the DB Tier.
On the DB tier there two main top level directories which are [dbname]DATA and [dbname]DB.
The [dbname]DATA is also reffred as the DATA_TOP contains all the datafiles (.dbf) for the various tablespaces of your database. These include your System tablespace, Applications Tablespace, Temporary table Space etc. All the datafiles must reside within the DATA_TOP.It is however possible to have multiple DATA_TOPs within a Oracle Applications Instance, this is
particularly useful for spreading across your datafiles across multiple mount points or disks.
The second important top level directory of the database tier is [dbname]DB. This contains your 9i ORACLE_HOME (as in the case of 11.5.10).That is under this directory all the files need to run and maintain you database reside.any database upgrade like upgrading your applications database to 10g would involve upgrading this ORACLE_HOME.
Coming to the Applications Tier there are three important top level directories.
[dbname]APPL,[dbname]COMN and [dbname]ORA
The [dbname]APPL is also know as your APPL_TOP. The APPL_TOP contains the core technology files required for Oracle Applications it also contains individual subdirectories for all oracle applications products. For eg under the [dbname]APPL or the APPL_TOP you would find directories for AD,FND,GL etc. These product directories are also know as PRODUCT_TOPs like AD_TOP,GL_TOP etc. Each of the product directories have the sub directories like admin, driver, import, odf, sql, bin, forms,reports etc.
The second TOP level directory under the applications tier is the [dbname]COMN. This is also referred to as your COMMON_TOP.The COMMON_TOP contains files that are commonly used by different Oracle applications products as well as any third party applications that may have been integrated with Oracle applications.
The COMMON_TOP contains sub following sub directories.
admin which holds the place for concurrent manager log and out files in the log and out sub directories respectively. Also it contains a scripts subdirectory.
html which is also referred by the environment variable OA_HTML contains the HTML files, JSP,CSS and Java scripts that are used by Oracle Applications.
java subdirectory which holds the jar files, this is also referred to as the JAVA_TOP.
scripts subdirectory that contains the machine admin scripts like the adstpall.sh
util subdirectory contains third party utilities that are used in oracle applications like JRE from sun microsystems
Temp subdirectory used for caching
Portal subdirectory used to delivery rapid install portal pages.
The third top level directory under application tier is the [dbname]ORA directory.This contains the IAS ORACLE HOME and the 8.0.6 ORACLE HOME.
Apart from the Database ORACLE_HOME 11i uses two other ORACLE_HOMES.The first is the 8.0.6 ORACLE HOME.This is used for developer 6i products which are forms reports and graphics. The applications executables also link with the 8.0.6 libraries.
IAS ORACLE HOME is the ORACLE HOME used by the 9iAS application server which is the primary web server for Oracle Applications.
Autoconfig
Autoconfig
An Oracle Applications instance has its configuration details that are stored and used in multiple files. Managing these configurations manually would have been a night mare without autoconfig. My friends who have worked with 11.0.3 and earlier versions would understand the pain better than anyone else. Though in 11.0.3 the number of configuration files were numbered and could be tracked with a little effort.
But not so in the case of 11i.Thankfully we have autoconfig to do up the messy job for us now.
Autoconfig is a utility which is shipped with the latest releases of Oracle Applications that manages all the configuration files in oracle Applications.
Autoconfig has been defined by oracle 'as a tool which that simplifies and standardizes configuration management tasks in an Oracle Applications environment'.
But where does autoconfig get the configuration information from? For this autoconfig relies on a file called the context file.
The context file is an XML file in the format [sid]_[hostname].xml.This xml file stores all the configuration details of your oracle applications system like the web port number, database names etc.
There are separate context files for the database tier and the applications tier.
The [context_name] variable used here is an equivalent of [sid]_[hostname]
The location of the context file on the application tier is
$APPL_TOP/admin/[context_name].xml
The location of the context file for the database tier is
$ORACLE_HOME/appsutil/[context_name].xml
Additionally if the applications is spread across multiple nodes each node will have its separate context file.
Autoconfig reads the information that is present in theses context files and updates the corresponding configuration files like appsweb.cfg, jserv.conf to name a couple.
But how do these context files get the information from? in previous versions of Oracle Applications we had a utility called the context editor which was used to update the context files. This has now been replaced by the Oracle Applications Manager.
Context files should now be edited only through OAM and never manually.
In case the context file is lost, you can regenerate your context file using the adbldxml.pl script
Once a particular context value is updated in OAM and saved, the changes are not propagated across the configuration files till you run autoconfig.
Apart form the context file autoconfig also makes use of the template files. Each configuration files that is going to be updated by autoconfig had a corresponding template file. Autoconfig compares the value from the context file with the template file before writing into the corresponding configuration file.
Driver files are also used by autoconfig, the driver files contain specific commands that may be required to be executed to update certain values at the database level.
Autoconfig is run by executing the shell script adautocfg.sh which in turn calls for the adconfig.sh which calls the perl script adconfig.pl.
The applications environment must be set before executing autoconfig, also since autoconfig will require a connection to your database you must ensure that the database and listener is up before running autoconfig.
Autoconfig is enabled in all latest releases of 11i,in case you want to implement autoconfig to an earlier 11i instance you can follow the instructions given in metalink note 165195.1
An Oracle Applications instance has its configuration details that are stored and used in multiple files. Managing these configurations manually would have been a night mare without autoconfig. My friends who have worked with 11.0.3 and earlier versions would understand the pain better than anyone else. Though in 11.0.3 the number of configuration files were numbered and could be tracked with a little effort.
But not so in the case of 11i.Thankfully we have autoconfig to do up the messy job for us now.
Autoconfig is a utility which is shipped with the latest releases of Oracle Applications that manages all the configuration files in oracle Applications.
Autoconfig has been defined by oracle 'as a tool which that simplifies and standardizes configuration management tasks in an Oracle Applications environment'.
But where does autoconfig get the configuration information from? For this autoconfig relies on a file called the context file.
The context file is an XML file in the format [sid]_[hostname].xml.This xml file stores all the configuration details of your oracle applications system like the web port number, database names etc.
There are separate context files for the database tier and the applications tier.
The [context_name] variable used here is an equivalent of [sid]_[hostname]
The location of the context file on the application tier is
$APPL_TOP/admin/[context_name].xml
The location of the context file for the database tier is
$ORACLE_HOME/appsutil/[context_name].xml
Additionally if the applications is spread across multiple nodes each node will have its separate context file.
Autoconfig reads the information that is present in theses context files and updates the corresponding configuration files like appsweb.cfg, jserv.conf to name a couple.
But how do these context files get the information from? in previous versions of Oracle Applications we had a utility called the context editor which was used to update the context files. This has now been replaced by the Oracle Applications Manager.
Context files should now be edited only through OAM and never manually.
In case the context file is lost, you can regenerate your context file using the adbldxml.pl script
Once a particular context value is updated in OAM and saved, the changes are not propagated across the configuration files till you run autoconfig.
Apart form the context file autoconfig also makes use of the template files. Each configuration files that is going to be updated by autoconfig had a corresponding template file. Autoconfig compares the value from the context file with the template file before writing into the corresponding configuration file.
Driver files are also used by autoconfig, the driver files contain specific commands that may be required to be executed to update certain values at the database level.
Autoconfig is run by executing the shell script adautocfg.sh which in turn calls for the adconfig.sh which calls the perl script adconfig.pl.
The applications environment must be set before executing autoconfig, also since autoconfig will require a connection to your database you must ensure that the database and listener is up before running autoconfig.
Autoconfig is enabled in all latest releases of 11i,in case you want to implement autoconfig to an earlier 11i instance you can follow the instructions given in metalink note 165195.1
AD Admin
AD Admin
Continuing our discussions on ad utilities today i will discuss about the most commonly used ad utility adadmin. Adadmin is a utility that performs a number of tasks required from maintaing and administering an Oracle Applications instance.
On a broad level the tasks performed by adadmin can be categorized into database activities and Applications filesystem management tasks.
In addition to these, adadmin in 11.5.10 onwards you can use adadmin to put the system in Maintenance Mode also. Maintenance mode is special mode introducted to facilitate maintenance tasks like patch application.
Before you run adadmin you must ensure the following.
Set your applications environment
Ensure that you have sufficient space in tmp disk.
For certain adadmin task you may require to shutdown your concurrent managers
You can run adadmin by typing adadmin at the command pront afdter seeting the environment.
$adadmin
At the time of execution adadmin prompts you to verify and enter several information pertaining to your applications installation like APPL_TOP location ,ORACLE_HOME.adadmin log file name,batch size etc.
Adadmin can also be run in a non interactive mode. This is accomplished by creating a defaults file.The defaults file must be place at the location $APPL_TOP/admin/[sid]/
You can create the defaults file with the following syntax
$adadmin deafultsfile=$APPL_TOP/admin/[sid]/samtask.txt
Next time you can run adadmin for the same task by specifying the interactive=no option.
adadmin \
defaultsfile=APPL_TOP/admin/vis/samtask.txt \
logfile=adadmin_091306.log workers=9 \
interactive=no
If your previous session of adadmin had encountred with problems adadmin promts you to either continue with your old session or start with a frest session as show below
Your previous AD Administration session did not run to completion.
Do you wish to continue with your previous AD Administration session [Yes] ?
The main menu of adadmin presents you with the following six choices
AD Administration Main Menu
--------------------------------------------------
1. Generate Applications Files menu
2. Maintain Applications Files menu
3. Compile/Reload Applications Database Entities menu
4. Maintain Applications Database Entities menu
5. Change Maintenance Mode
6. Exit AD Administration
First two options are related to maintaining applications file system the second twop options relate to database activities ,the fifth option here is used to put the system in maintenance mode and bring it back from maintenance mode.
Under the Generate Applications Files Menu you can perform the following tasks
Generate Applications Files
----------------------------------------
1. Generate message files
2. Generate form files
3. Generate report files
4. Generate graphics files
5. Generate product JAR files
6. Return to Main Menu
Under the Maintain Applications Files menu you can perform the following tasks
Maintain Applications Files
----------------------------------------
1. Relink Applications programs
2. Create Applications environment file
3. Copy files to destinations
4. Convert character set
5. Maintain snapshot information
6. Check for missing files
7. Return to Main Menu
Under the Compile/Reload Applications Database Entities menu you can perform the following tasks
Compile/Reload Applications Database Entities
---------------------------------------------------
1. Compile APPS schema
2. Compile menu information
3. Compile flexfields
4. Reload JAR files to database
5. Return to Main Menu
Under the Maintain Applications Database Entities menu you can perform the following tasks
Maintain Applications Database Entities
---------------------------------------------------
1. Validate APPS schema
2. Re-create grants and synonyms for APPS schema
3. Maintain multi-lingual tables
4. Check DUAL table
5. Maintain Multiple Reporting Currencies schema
6. Return to Main Menu
Under the Change Maintenance Mode you can do the following
Change Maintenance Mode
----------------------------------------
Maintenance Mode is currently: [Disabled].
Maintenance mode should normally be enabled when patching
Oracle Applications and disabled when users are logged on
to the system. See the Oracle Applications Maintenance
Utilities manual for more information about maintenance mode.
Please select an option:
1. Enable Maintenance Mode
2. Disable Maintenance Mode
3. Return to Main Menu
If you noitice the message this menu selection also shows the maintenance status (disabled in our case) of the system.
You can also forcefully exit adadmin at any point of time by typing 'abort',This will however result in a unclean exit of adadmin and the next time when you run adadmin you will be prompted with the option to start fresh or continue with the previous session as described earlier
To know more about the individual tasks performed by admin refer to the 'Maintaining Oracle Applications Documentation Set' at the applications documentation library.
Continuing our discussions on ad utilities today i will discuss about the most commonly used ad utility adadmin. Adadmin is a utility that performs a number of tasks required from maintaing and administering an Oracle Applications instance.
On a broad level the tasks performed by adadmin can be categorized into database activities and Applications filesystem management tasks.
In addition to these, adadmin in 11.5.10 onwards you can use adadmin to put the system in Maintenance Mode also. Maintenance mode is special mode introducted to facilitate maintenance tasks like patch application.
Before you run adadmin you must ensure the following.
Set your applications environment
Ensure that you have sufficient space in tmp disk.
For certain adadmin task you may require to shutdown your concurrent managers
You can run adadmin by typing adadmin at the command pront afdter seeting the environment.
$adadmin
At the time of execution adadmin prompts you to verify and enter several information pertaining to your applications installation like APPL_TOP location ,ORACLE_HOME.adadmin log file name,batch size etc.
Adadmin can also be run in a non interactive mode. This is accomplished by creating a defaults file.The defaults file must be place at the location $APPL_TOP/admin/[sid]/
You can create the defaults file with the following syntax
$adadmin deafultsfile=$APPL_TOP/admin/[sid]/samtask.txt
Next time you can run adadmin for the same task by specifying the interactive=no option.
adadmin \
defaultsfile=APPL_TOP/admin/vis/samtask.txt \
logfile=adadmin_091306.log workers=9 \
interactive=no
If your previous session of adadmin had encountred with problems adadmin promts you to either continue with your old session or start with a frest session as show below
Your previous AD Administration session did not run to completion.
Do you wish to continue with your previous AD Administration session [Yes] ?
The main menu of adadmin presents you with the following six choices
AD Administration Main Menu
--------------------------------------------------
1. Generate Applications Files menu
2. Maintain Applications Files menu
3. Compile/Reload Applications Database Entities menu
4. Maintain Applications Database Entities menu
5. Change Maintenance Mode
6. Exit AD Administration
First two options are related to maintaining applications file system the second twop options relate to database activities ,the fifth option here is used to put the system in maintenance mode and bring it back from maintenance mode.
Under the Generate Applications Files Menu you can perform the following tasks
Generate Applications Files
----------------------------------------
1. Generate message files
2. Generate form files
3. Generate report files
4. Generate graphics files
5. Generate product JAR files
6. Return to Main Menu
Under the Maintain Applications Files menu you can perform the following tasks
Maintain Applications Files
----------------------------------------
1. Relink Applications programs
2. Create Applications environment file
3. Copy files to destinations
4. Convert character set
5. Maintain snapshot information
6. Check for missing files
7. Return to Main Menu
Under the Compile/Reload Applications Database Entities menu you can perform the following tasks
Compile/Reload Applications Database Entities
---------------------------------------------------
1. Compile APPS schema
2. Compile menu information
3. Compile flexfields
4. Reload JAR files to database
5. Return to Main Menu
Under the Maintain Applications Database Entities menu you can perform the following tasks
Maintain Applications Database Entities
---------------------------------------------------
1. Validate APPS schema
2. Re-create grants and synonyms for APPS schema
3. Maintain multi-lingual tables
4. Check DUAL table
5. Maintain Multiple Reporting Currencies schema
6. Return to Main Menu
Under the Change Maintenance Mode you can do the following
Change Maintenance Mode
----------------------------------------
Maintenance Mode is currently: [Disabled].
Maintenance mode should normally be enabled when patching
Oracle Applications and disabled when users are logged on
to the system. See the Oracle Applications Maintenance
Utilities manual for more information about maintenance mode.
Please select an option:
1. Enable Maintenance Mode
2. Disable Maintenance Mode
3. Return to Main Menu
If you noitice the message this menu selection also shows the maintenance status (disabled in our case) of the system.
You can also forcefully exit adadmin at any point of time by typing 'abort',This will however result in a unclean exit of adadmin and the next time when you run adadmin you will be prompted with the option to start fresh or continue with the previous session as described earlier
To know more about the individual tasks performed by admin refer to the 'Maintaining Oracle Applications Documentation Set' at the applications documentation library.
Shared APPL_TOP and Application Tier Filesystem
Shared APPL_TOP and Application Tier Filesystem
In the Shared APPL_TOP feature introduced by Oracle in E-Business 11i, Oracle allows multiple nodes to share a single APPL_TOP .In a shared APPL_TOP configuration, the APPL_TOP and COMN_TOP file systems can be installed on a single shared disk. The shared disk resource can then be shared via various network file protocols across multiple nodes to provide standard application tier services such as forms, web and concurrent processing. A shared APPL_TOP also significantly simplifies the patching or upgrade process since it has to be performed only once and changes made are immediately visible to all the nodes.
Here it is important to note that there is a difference between a Shared APPL_TOP and a Shared Application Tier File system. In a Shared APPL_TOP though the APPL_TOP(APPL_TOP and the COMMON_TOP ) is shared across different nodes, each nodes still have their individual ORACLE_HOME. In a Shared Application Tier FileSystem both the APPL_TOP and the ORACLE_HOME (ORA_TOP) reside on the shared disk.
The Shared APPL_TOP architecture was introduced in 2003 however with the release of 11.5.10 Oracle has extended this feature to share the entire application tier filesystem thereby further reducing disk space and bring down maintenance tasks.This is what is referred to now as the Shared Application Tier File System.
This feature i found to be particularly useful if your oracle applications environment uses multiple languages. Using the Shares APPL_TOP feature i do not now have to apply the translation on all the application Tier nodes but just to the Shared APPL_TOP.
In both the cases any changes on the shared TOPs like for example patch application is immediately visible to all the nodes of the application tier.
Another important factor to be kept in mind is that SHARED APPL_TOPS will not work if different nodes are on different Operating systems. So its mandatory that the different nodes of the application tier run on a same operating system or in other words the different nodes must be binary compatible.
Also as of now the SHARED APPL_TOP feature is not available for the windows version of Oracle Applications.
Apart from reducing maintenance tasks a shared APPL_TOP/Shared Application Tier Filesystem also improves scalability of the system as it less complex to bring in an additional node to improve performance.
There are various methods by with you can implement shared APPL_TOP like using Rapid Install or by merging existing APPL_TOPs.
It is mandatory for you to have implemented autoconfig before you can proceed with the implementation of a Shared APPL_TOP.
The metalink note Sharing the Application Tier File System in Oracle Applications 11i 233428.1 talks about implementing shared APPL_TOP under different Scenarios.
While patching a shared APP_TOP you can just apply the path to any of the nodes and it will become visible to all the nodes, in case of applying a patch to 8.0.6 home or IAS_HOME you need to apply the patch only once but to a primary node.
Shared APPL_TOP and Shared Application Files system concepts are different from a Staged APPL_TOP. A Staged APPL_TOP is implemented to reduce your patching related downtimes by creating a exact clone of your production system, patching that system and synchronizing your cloned at database and application level to the production system.
This approach significantly reduceds your patching downtime.
To know more about a Staged APPL_TOP refer to metalink note 242480.1
In the Shared APPL_TOP feature introduced by Oracle in E-Business 11i, Oracle allows multiple nodes to share a single APPL_TOP .In a shared APPL_TOP configuration, the APPL_TOP and COMN_TOP file systems can be installed on a single shared disk. The shared disk resource can then be shared via various network file protocols across multiple nodes to provide standard application tier services such as forms, web and concurrent processing. A shared APPL_TOP also significantly simplifies the patching or upgrade process since it has to be performed only once and changes made are immediately visible to all the nodes.
Here it is important to note that there is a difference between a Shared APPL_TOP and a Shared Application Tier File system. In a Shared APPL_TOP though the APPL_TOP(APPL_TOP and the COMMON_TOP ) is shared across different nodes, each nodes still have their individual ORACLE_HOME. In a Shared Application Tier FileSystem both the APPL_TOP and the ORACLE_HOME (ORA_TOP) reside on the shared disk.
The Shared APPL_TOP architecture was introduced in 2003 however with the release of 11.5.10 Oracle has extended this feature to share the entire application tier filesystem thereby further reducing disk space and bring down maintenance tasks.This is what is referred to now as the Shared Application Tier File System.
This feature i found to be particularly useful if your oracle applications environment uses multiple languages. Using the Shares APPL_TOP feature i do not now have to apply the translation on all the application Tier nodes but just to the Shared APPL_TOP.
In both the cases any changes on the shared TOPs like for example patch application is immediately visible to all the nodes of the application tier.
Another important factor to be kept in mind is that SHARED APPL_TOPS will not work if different nodes are on different Operating systems. So its mandatory that the different nodes of the application tier run on a same operating system or in other words the different nodes must be binary compatible.
Also as of now the SHARED APPL_TOP feature is not available for the windows version of Oracle Applications.
Apart from reducing maintenance tasks a shared APPL_TOP/Shared Application Tier Filesystem also improves scalability of the system as it less complex to bring in an additional node to improve performance.
There are various methods by with you can implement shared APPL_TOP like using Rapid Install or by merging existing APPL_TOPs.
It is mandatory for you to have implemented autoconfig before you can proceed with the implementation of a Shared APPL_TOP.
The metalink note Sharing the Application Tier File System in Oracle Applications 11i 233428.1 talks about implementing shared APPL_TOP under different Scenarios.
While patching a shared APP_TOP you can just apply the path to any of the nodes and it will become visible to all the nodes, in case of applying a patch to 8.0.6 home or IAS_HOME you need to apply the patch only once but to a primary node.
Shared APPL_TOP and Shared Application Files system concepts are different from a Staged APPL_TOP. A Staged APPL_TOP is implemented to reduce your patching related downtimes by creating a exact clone of your production system, patching that system and synchronizing your cloned at database and application level to the production system.
This approach significantly reduceds your patching downtime.
To know more about a Staged APPL_TOP refer to metalink note 242480.1
Oracle Jinitiator
Oracle Jinitiator
Oracle Applications is based upon a thin client architecture. On the desktop Tier you need almost nothing.. Well almost, it does require a certified web browser and the Oracle Jinitiator.
Oracle Jinitiator is a software that provides the JVM to run oracle form based products which run in the form of a form client applet.The oracle Jinitiator uses its own JVM instead of the browsers JVM.It is isntalled as a plugin ( as in the case of mozilla, Netscape or firefox) or as an Active X component (in case of Internet Explorer).
When Oracle Applications is accessed for the first time from a client PC the Jinitiator is downloaded and installed on the client PC.It is not used for Self Service Web Applications, The JInitiator is invoked only upon clicking a form based application.
After Jinitiator is installed it downloads the form client applet along with the commonly used JAR files, this is done to reduce the network traffic to download JAR files form the server every time.
Jinitiator also performs JAR caching, applet caching and incremental JAR loading to improve applications performance.
These JAR files are commonly stored under the users profile directory with a folder named Oracle Jar Cache.
The Oracle Jinitiator executable is stored on the location $OA_HTML/oajinit.exe
Oracle Jinitiator allows only trusted JAR files to run within its JVM. This trust is established by using digital signatures. In the current version of Oracle Applications the JAR files are automatically signed with the digital signatures during the install of Oracle Applications using rapidwiz. However you can still change your digital signature and repackage your oajinit.exe for security reasons.
During the installation process rapidwiz automatically creates a file in the applmgr user $HOME directory called identitydb.obj, this file has a reference to the SID of the database instance.
If there is a mismatch between this file on the server and that on the clinet PC it often results in the yellow bar problem.
The following files are created automatically by rapidwiz in the current version of Oracle Applications
$APPL_TOP/admin/appltop.cer
$APPL_TOP/admin/adsign.txt
$HOME(applmgr)/identitydb.obj
To create a new digital certificate you can use the adjkey command, while the adjbuild.sh is used to repackage your jinitiator exe.You can also regenerate your JAR files using ADADMIN.
A Jinitiator package should typically contain the certificate and the obj file along with the executable.
In previous versions of Oracle Applications (earlier to 11.5.9) an unsigned JAR file would result in a yellow bar problem, but in the current release of Oracle Application attempting to load a forms with an unsigned JAR file would fail with an a java security exception error.
The latest certified versions of Oracle Jinitiator is 1.3.1.26 to run with Oracle E-business Suite 11.5.10, the least certified version is 1.1.8.16 which is used with release 11, though you can use version 1.1.8.X to access your 11i applications it is recommended that you upgrade your Jinitiator to the latest supported version 1.3.1.X.
You can follow the metalink note id 124606.1 to upgrade your Jinitiator.
An important fact to remember is that any patch applied through adpatch which contains JAR files, these new JAR files are not signed with the digital signature, after the patch is applied adpatch will regenerate all the JAR files and these new JAR files will be signed and trusted to run within the Jinitiator.
To see a list of supported browsers that are certified to access E-Business Suite reffer to metalink Note id 285218.1.
Oracle Applications is based upon a thin client architecture. On the desktop Tier you need almost nothing.. Well almost, it does require a certified web browser and the Oracle Jinitiator.
Oracle Jinitiator is a software that provides the JVM to run oracle form based products which run in the form of a form client applet.The oracle Jinitiator uses its own JVM instead of the browsers JVM.It is isntalled as a plugin ( as in the case of mozilla, Netscape or firefox) or as an Active X component (in case of Internet Explorer).
When Oracle Applications is accessed for the first time from a client PC the Jinitiator is downloaded and installed on the client PC.It is not used for Self Service Web Applications, The JInitiator is invoked only upon clicking a form based application.
After Jinitiator is installed it downloads the form client applet along with the commonly used JAR files, this is done to reduce the network traffic to download JAR files form the server every time.
Jinitiator also performs JAR caching, applet caching and incremental JAR loading to improve applications performance.
These JAR files are commonly stored under the users profile directory with a folder named Oracle Jar Cache.
The Oracle Jinitiator executable is stored on the location $OA_HTML/oajinit.exe
Oracle Jinitiator allows only trusted JAR files to run within its JVM. This trust is established by using digital signatures. In the current version of Oracle Applications the JAR files are automatically signed with the digital signatures during the install of Oracle Applications using rapidwiz. However you can still change your digital signature and repackage your oajinit.exe for security reasons.
During the installation process rapidwiz automatically creates a file in the applmgr user $HOME directory called identitydb.obj, this file has a reference to the SID of the database instance.
If there is a mismatch between this file on the server and that on the clinet PC it often results in the yellow bar problem.
The following files are created automatically by rapidwiz in the current version of Oracle Applications
$APPL_TOP/admin/appltop.cer
$APPL_TOP/admin/adsign.txt
$HOME(applmgr)/identitydb.obj
To create a new digital certificate you can use the adjkey command, while the adjbuild.sh is used to repackage your jinitiator exe.You can also regenerate your JAR files using ADADMIN.
A Jinitiator package should typically contain the certificate and the obj file along with the executable.
In previous versions of Oracle Applications (earlier to 11.5.9) an unsigned JAR file would result in a yellow bar problem, but in the current release of Oracle Application attempting to load a forms with an unsigned JAR file would fail with an a java security exception error.
The latest certified versions of Oracle Jinitiator is 1.3.1.26 to run with Oracle E-business Suite 11.5.10, the least certified version is 1.1.8.16 which is used with release 11, though you can use version 1.1.8.X to access your 11i applications it is recommended that you upgrade your Jinitiator to the latest supported version 1.3.1.X.
You can follow the metalink note id 124606.1 to upgrade your Jinitiator.
An important fact to remember is that any patch applied through adpatch which contains JAR files, these new JAR files are not signed with the digital signature, after the patch is applied adpatch will regenerate all the JAR files and these new JAR files will be signed and trusted to run within the Jinitiator.
To see a list of supported browsers that are certified to access E-Business Suite reffer to metalink Note id 285218.1.
AD Splicer
AD Splicer
Oracle Applications provides quite a few utilities which are aimed at effective maintenance and monitoring an Oracle Applications instance. In my next posts i will talk about these UNIX utilities which are also referred to as AD utilities.
Today i used AD Splicer so i will start with this one.
AD Splicer is a utility used to add an off-cycle product into Oracle Applications.
Products which have been released between the base releases of 11i are referred to an off-cycle product. Once AD Splicer is used to splice these off-cycle products into Oracle Applications they are recognized by other AD utilities like AD Patch as a valid Oracle Applications product for a given release.
In a multi node environment adsplicer should be used on all the APPL_TOPs.It is recommended to run AD Splice on the Admin node first.
Before using AD Splice you are required to add the new tablespace for the new products that are going to be added. In case you have migrated to the Oracle Applications new tablespace model you would require to create a new tablespace APPS_TS_TOOLs manually before using AD Splicer.
Ad Splicer makes use of the following control files to add the new off-cycle product into oracle applications.
[prod]prod.txt : This is a product definition file which contains the language independent information about the product.
[prod]terr.txt : This is also a product definition file containing language-specific information about the new product.
Both these product definition files should not be edited manually.
For example the product definition files for the off-cycle product Web ADI are bneterr.txt and bneprod.txt
newprods.txt : This file is also know as the product configuration file. You can edit this file optionally.
This file acts as a template for configuring the new product that would be added. It comprises of a list of parameters which include
product- The product being added eg.bne .This must not be changed.
base_product_top - This is the base path where the files for the new product will be places using the Oracle applications filesystem architecture. the default value for this is APPL_TOP.
oracle_schema - This parameter refer to the oracle schema which is the owner of the new product to be added.
sizing_factor - The sizing factor which is to be followed for table and index creation.
main_tspace - The tablespace for product tables
index_tspace - The tablespace for product indexes
temp_tspace - The tablespace for Oracle schema’s temporary segments
default_tspace - This refers to the default table space for the of the Oracle Schema owning the product.
All the above mentioned control files namely the prod.txt,terr.txt and newprods.txt must be placed in $APPL_TOP/admin so that adsplce is able to read them.
Like other Ad utilities AD Splice will also require to make a connection to your database instance using SYSTEM and APPLSYS accounts as a result your database and listener must be running while using AD Splice.
An important fact to note is that products that are added through AD Splice are visible to other AD Utilites except autoupgrade.
The metalink Note 76708.1 contains further details and instructions on using AD Splice
Oracle Applications provides quite a few utilities which are aimed at effective maintenance and monitoring an Oracle Applications instance. In my next posts i will talk about these UNIX utilities which are also referred to as AD utilities.
Today i used AD Splicer so i will start with this one.
AD Splicer is a utility used to add an off-cycle product into Oracle Applications.
Products which have been released between the base releases of 11i are referred to an off-cycle product. Once AD Splicer is used to splice these off-cycle products into Oracle Applications they are recognized by other AD utilities like AD Patch as a valid Oracle Applications product for a given release.
In a multi node environment adsplicer should be used on all the APPL_TOPs.It is recommended to run AD Splice on the Admin node first.
Before using AD Splice you are required to add the new tablespace for the new products that are going to be added. In case you have migrated to the Oracle Applications new tablespace model you would require to create a new tablespace APPS_TS_TOOLs manually before using AD Splicer.
Ad Splicer makes use of the following control files to add the new off-cycle product into oracle applications.
[prod]prod.txt : This is a product definition file which contains the language independent information about the product.
[prod]terr.txt : This is also a product definition file containing language-specific information about the new product.
Both these product definition files should not be edited manually.
For example the product definition files for the off-cycle product Web ADI are bneterr.txt and bneprod.txt
newprods.txt : This file is also know as the product configuration file. You can edit this file optionally.
This file acts as a template for configuring the new product that would be added. It comprises of a list of parameters which include
product- The product being added eg.bne .This must not be changed.
base_product_top - This is the base path where the files for the new product will be places using the Oracle applications filesystem architecture. the default value for this is APPL_TOP.
oracle_schema - This parameter refer to the oracle schema which is the owner of the new product to be added.
sizing_factor - The sizing factor which is to be followed for table and index creation.
main_tspace - The tablespace for product tables
index_tspace - The tablespace for product indexes
temp_tspace - The tablespace for Oracle schema’s temporary segments
default_tspace - This refers to the default table space for the of the Oracle Schema owning the product.
All the above mentioned control files namely the prod.txt,terr.txt and newprods.txt must be placed in $APPL_TOP/admin so that adsplce is able to read them.
Like other Ad utilities AD Splice will also require to make a connection to your database instance using SYSTEM and APPLSYS accounts as a result your database and listener must be running while using AD Splice.
An important fact to note is that products that are added through AD Splice are visible to other AD Utilites except autoupgrade.
The metalink Note 76708.1 contains further details and instructions on using AD Splice
Faster database exports/imports
Faster database exports/imports
The import and export programs (imp/exp) run in two task mode to protect the SGA from potential corruption by user programs. By relinking these two programs in single task mode you can gain much improvement in speed. In many cases up to 30%. Oracle themselves use this method although it is NOT supported by Oracle.
Running in single-task is much faster but it requires more memory since the Oracle executable's text is no longer shared between the front-end and background processes. If you need to transfer large amounts of data between databases, relink the executale for greater efficiency.
To relink the RDBMS kernel and create the two new imp/exp programs, use the following:
% cd $ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/lib
% make -f ins_rdbms.mk singletask
% make -f ins_rdbms.mk expst
% make -f ins_rdbms.mk impst
% make -f ins_rdbms.mk sqlldrst
% mv expst $ORACLE_HOME/bin/
% mv impst $ORACLE_HOME/bin/
% mv sqlldrst $ORACLE_HOME/bin/
Now use expst and impst instead of imp or exp.
The import and export programs (imp/exp) run in two task mode to protect the SGA from potential corruption by user programs. By relinking these two programs in single task mode you can gain much improvement in speed. In many cases up to 30%. Oracle themselves use this method although it is NOT supported by Oracle.
Running in single-task is much faster but it requires more memory since the Oracle executable's text is no longer shared between the front-end and background processes. If you need to transfer large amounts of data between databases, relink the executale for greater efficiency.
To relink the RDBMS kernel and create the two new imp/exp programs, use the following:
% cd $ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/lib
% make -f ins_rdbms.mk singletask
% make -f ins_rdbms.mk expst
% make -f ins_rdbms.mk impst
% make -f ins_rdbms.mk sqlldrst
% mv expst $ORACLE_HOME/bin/
% mv impst $ORACLE_HOME/bin/
% mv sqlldrst $ORACLE_HOME/bin/
Now use expst and impst instead of imp or exp.
Sunday, June 8, 2008
Concurrent Manager Q and A
Concurrent Manager Questions and Answers Relating to Generic Platform
PURPOSE
-------
To deliver a set of frequently asked questions against AOL FND Concurrent
Manager.
SCOPE & APPLICATION
-------------------
This reference would be most useful for one who is seeking additional
information regarding AOL FND Concurrent Manager issues.
FND Concurrent Manager FAQ's
-----------------------------
When would one be required to bounce (stop and restart) the Concurrent Manager?
When you modify the Printer Driver you have to restart the Manager which
runs the request which is attached to that Printer Driver, however,if you do
not know which manager then you have to restart the Internal manager because
the printer driver can be used by multiple managers and multiple requests.
If only a concurrent program definition is modified, running a verify on the
Internal Manager will pick up the changes without the need for bouncing the
manager.
Does the Internal manager schedule requests to be run or does it put requests
into queues to be run by other managers?
This is a very common misconception. The ICM really does not have any
such scheduling responsibilities. It has NOTHING to do with scheduling
requests, or deciding which manager will run a particular request.
Its function is only to run 'queue control' requests, which are
requests to startup or shutdown other managers. It is responsible for
startup and shutdown of the whole concurrent processing facility, and
it also monitors the other managers periodically, and restarts them if
they should go down. It can also take over the Conflict Resolution
manager's job, and resolve incompatibilities.
If the ICM itself should go down, requests will continue to run
normally, except for 'queue control' requests. You can restart it with
'startmgr', you do not need to kill the other managers first.
How can I check to see if a concurrent manager is running?
One way to see if a manager is running is to use the 'Administer
Concurrent Managers' form. Navigate to Concurrent->Managers->Administer.
You will see two columns labeled 'Actual' and 'Target'. The Target column
lists the number of processes that should be running for each manager
for this particular workshift. The Actual column lists the number of
processes that are actually running. If the Actual column is zero, there
are no processes running for this manager. If the Target column is zero,
then either a workshift has not been assigned to this manager, or the current
workshift does not specify any target processes. If the target column
is not zero, then the manager processes have either failed to start up,
or gone down. You should check the manager's logfile and the ICM
logfile. You can also search for OS processes using the 'ps' command.
It is possible for the form to be inaccurate, i.e. it may show actual
processes even though they are not really running. When in doubt, check for
processes at the OS level. On NT, you can check to see if the Concurrent Manager
service is running using the Services control panel.
Where do concurrent request or manager logfiles and output files go?
The concurrent manager first looks for the environment variable
$APPLCSF. If this is set, it creates a path using two other
environment variables: $APPLLOG and $APPLOUT
It places log files in $APPLCSF/$APPLLOG, output files go in
$APPLCSF/$APPLOUT
So for example, if you have this environment set:
$APPLCSF = /u01/appl/common
$APPLLOG = log
$APPLOUT = out
The concurrent manager will place log files in /u01/appl/common/log,
and output files in /u01/appl/common/out
Note that $APPLCSF must be a full, absolute path, and the other two
are directory names.
If $APPLCSF is not set, it places the files under the product top of
the application associated with the request. For example, a PO report
would go under $PO_TOP/$APPLLOG and $PO_TOP/$APPLOUT
Logfiles go to: /u01/appl/po/9.0/log
Output files to: /u01/appl/po/9.0/out
All these directories must exist and have the correct permissions.
Note that all concurrent requests produce a log file, but not necessarily
an output file.
Concurrent manager logfiles follow the same convention, and will be
found in the $APPLLOG directory
What are the logfile and output file naming conventions?
Request logfiles: l.req
Output files: If $APPCPNAM is not set:.
If $APPCPNAM = REQID: o.out
If $APPCPNAM = USER:.out
Where: = The request id of the concurrent request
And: = The id of the user that submitted the request
Manager logfiles:
ICM logfile: Default is std.mgr, can be changed with the mgrname
startup parameter
Concurrent manager log: w.mgr
Transaction manager log: t.mgr
Conflict Resolution manager log: c.mgr
Where: is the concurrent process id of the manager
Can I delete a concurrent manager?
You can disable the manager by checking the 'Enabled' checkbox, or
you can simply Terminate the manager and it will not run again unless
you reactivate it.
If it is really necessary, you can query the manager in the
'Define Manager' form, and delete the row. (It is recommended that you
DO NOT do this)
What is the function of the 'Conflict Resolution Manager'?
Concurrent managers read requests to start concurrent programs running. The
Conflict Resolution Manager checks concurrent program definitions for
incompatibility rules.
If a program is identified as Run Alone, then the Conflict Resolution Manager
prevents the concurrent managers from starting other programs in the same
conflict domain.
When a program lists other programs as being incompatible with it, the
Conflict Resolution Manager prevents the program from starting until any
incompatible programs in the same domain have completed running.
What is the 'Internal Scheduler/Prereleaser' manager?
The short name for this manager is FNDSCH. It is also known as the
Advanced Scheduler/Prereleaser Manager. This manager is intended
to implement Advanced Schedules. Its job is to determine when a
scheduled request is ready to run. Advanced Schedules were not fully
implemented in Release 11.0, they are implemented in Release 11.5,
but are not widely used by the various Apps products. General Ledger
uses FNDSCH for financial schedules based on different calendars and
period types. It is then possible to schedule AutoAllocation sets,
Recurring Journals, MassAllocations, Budget Formulas, and MassBudgets
to run according to the General Ledger schedules that have been
defined.
If financial schedules in GL are not being used then it is not a
problem to deactivate this manager.
What is the 'Internal Monitor' manager/service?
This manager/service is used to implement Distributed Concurrent Processing.
It monitors whether the ICM is still running, and if the ICM crashes,
it will restart it on another node.
You do not need to run this manager/service unless you are using Distributed
Concurrent Processing.
See the Installation manual and Sysadmin Guide for more info on DCP.
How do I check/set the PMON method?
To check the PMON method:
1) cd $FND_TOP/sql
2) sqlplus apps/apps @afimchk.sql
This will tell whether the internal manager is running, what the PMON
method is, and where the log file is.
To set the PMON method:
1) first shut the concurrent managers down
2) cd $FND_TOP/sql
3) sqlplus apps/apps @afimpmon.sql LOCK (or RDBMS)
How do I enable/disable the Conflict Resolution Manager?
Use the system profile option 'Concurrent: Use ICM'.
Setting this to 'No' (which is the default) allows the CRM to be started.
Setting it to 'Yes' causes the CRM to be shutdown and the Internal
Manager (ICM) will take over the conflict resolution duties. If the CRM will
not start (it is started automatically by the ICM), check this profile option.
Note that using the ICM to resolve conflicts is not recommended.
The CRM's sole purpose is to resolve conflicts, while the ICM has
other functions to perform as well. Only set this option to 'YES'
if you have a good reason to do so.
How do I clean out the Concurrent Manager tables?
Cleaning out the tables is a useful method of making sure that there
are no invalid statuses that can prevent the managers from starting.
Previously, this has been done by truncating fnd_concurrent_processes
and/or fnd_concurrent_requests. Truncation of the tables is a little
drastic, and can cause problems later when trying to purge requests,
not to mention losing all of the request information.
Run the script, cmclean.sql, article Note 134007.1 CMCLEAN.SQL - Non
Destructive Script to Clean Concurrent Manager Tables
It will make sure the relevant status codes are valid without
deleting any information.
How do I tell concurrent manager processes apart at the OS level?
Use: pf -ef | grep FNDLIBR
This will produce output like:
vd11 13703 13660 0 May 11 ? 0:01 FNDLIBR FND Concurrent_Processor
MANAGE OLOGIN="APPS/94A491A1000000000000000000
n1070161 24936 24927 0 Apr 29 ? 0:05 FNDLIBR FND Concurrent_Processor
MANAGE OLOGIN="APPS_APPDEMO/94C4B1C10000000000
n1070161 24938 24927 0 Apr 29 ? 0:06 FNDLIBR FND Concurrent_Processor
MANAGE OLOGIN="APPS_APPDEMO/94C4B1C10000000000
n1070161 24927 24922 0 Apr 29 ? 2:03 FNDLIBR FND CPMGR FNDCPMBR sysmgr
="" sleep=60 pmon=20 diag=N logfile=/u16/app
The last process, #24927, shows 'FNDLIBR FND CPMGR', this one is the
Internal Manager (ICM). Notice that it gives some of the parameters it
was started with, the other processes showing 'Concurrent_Processor'
are Standard manager processes. Notice that the ICM process is the
parent process of the Standard managers. (processes 24936 and 24938)
Other managers will have the name of the executable, like ARLIBR or
INVLIBR:
$ ps -ef | grep ARLIBR
vd11 13683 13660 0 May 11 ? 0:20 ARLIBR APPS/82A2A4940000000000000
000000000000000000000000000000000000000 AR ART
The Conflict Resolution manager will look like:
$ ps -ef | grep FNDCRM
n1070161 24941 24927 0 Apr 29 ? 1:17 FNDCRM APPS_APPDEMO/84BFBEB900000
0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
What is the syntax for controlling the concurrent manager using startmgr and
concsub in NT?
On NT, the concurrent manager is run as an NT service, you start and
stop the managers using the Services control panel.
See the Applications Installation manual for NT, Appendix A for
details. See pg. 5-9 of this manual for instructions on creating the
concurrent manager service.
Why am I seeing pinging entries like this in the ICM logfile?
PING (0.0.0.0): 56 data bytes
64 bytes from 192.75.91.2: icmp_seq=0 ttl=255 time=0.705 ms
64 bytes from 192.75.91.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=255 time=1.120 ms
Process monitor session ended : 29-FEB-2000 10:38:43
64 bytes from 192.75.91.2: icmp_seq=2 ttl=255 time=0.985 ms
64 bytes from 192.75.91.2: icmp_seq=3 ttl=255 time=1.006 ms
Pinging other machines is used in Distributed Concurrent Processing.
This means you have DCP turned on, using the environment variable
APPLDCP. Set APPLDCP to OFF and restart the managers.
I hit the Restart button to start the Standard manager, but it still did not
start?
Telling a manager to restart just sets the status to Restart. The ICM
will start it the next process monitor session or the next time the
ICM starts. Use Activate to start a manager immediately.
When a manager is deactivated manually, the ICM will not restart
it, you will need to set it to Restart, or activate it manually.
How many rows are in FND_CONCURRENT_REQUESTS and FND_CONCURRENT_PROCESSES
tables?
When tables reach above 3000-4000 rows, the performance begins to
diminish. You may want to run Purge Concurrent Request on a regular basis,
dependant on the amount of requests being run.
The Purge Concurrent Requests job can be used to purge:
Requests, Mgr logs, and All requests depending on what is chosen.
Use the following options: Enter = All, Mode = AGE, Mode Value = 15
The std.mgr log continuously grows where it may good to
archive it regularly.
Any processes pending in Internal or Conflict Resolution Manager?
Best course of action before starting the Concurrent Managers is to cancel
any "Deactivate" or "Verify" jobs pending in the Internal Manager and place
any other pending jobs on hold.
How do I turn on transaction manager diagnostics?
Set the profile option 'Concurrent:Debug Flags' to 'TCTM1' at the site
level. This will cause transactions to make debug entries in the
FND_CONCURRENT_DEBUG_INFO table. Truncate this table before running a
tranasction, then select the entries from the table.
Starting the managers with diag=Y will also produce more information
in the transaction manager logfile.
How do transaction managers work?
Briefly:
(See the server documentation for details on the DBMS_PIPE package)
1) A tranasction manager is started on the concurrent processing
server, and periodically reads the pipe for incoming transactions.
2) A client program (usually a form) calls the
FND_TRANSACTION.SYNCHRONOUS function.
3) This function writes a message into the pipe containing the program
to be run and its parameters.
4) FND_TRANSACTION.SYNCHRONOUS begins reading a return pipe for the
return status.
5) The manager sees the message in the pipe, retrieves the program id
and parameters.
6) The manager runs the program with the specified parameters. The
program will be of type 'Immediate', so there will not be a
separate concurrent request run.
7) The program completes, and the manager packs its return status into
the return pipe.
8) FND_TRANSACTION.SYNCHRONOUS reads the return value and passes it
back to its caller.
Note that these events take place essentially simultaneously on the
client and server. This is a synchronous transaction because the
client waits for the server to return, or times out waiting for it.
Problem....
When you try to submit a request like Active users or
Active responsibilities, request gets submitted.
When we view the help requests, you find that it is
inactive / nomanager.
Within 12 to 15 seconds, you refresh-it gets completed.
Initially, you could find only inactive and we look at
the diagnostic- the concurrent manager assigned is not
picking up.
There is no specialization rules in any managers except
the include program this source.
Solution....
Most often when this occurs where a request goes
"inactive/no manager" and is then processed a short time
later, the solution is to either increase the cache size
for your Standard manger, or increase the actual number of
Standard manager processes.
Cache Size is set on the CONCURRENT/MANAGER/DEFINE form. Basically,
this regulates how many requests a manager will pick up for each
sleep cycle.
How do I process more concurrent requests concurrently?
The Concurrent Manager parameters, (Query the concurrent manager by
Login as Sysadmin, navigate -> Concurrent -> Manager -> Define and Query for
the relevant concurrent manager), should be modified to handle more
concurrent requests concurrently, this can be done in two steps:
(i) Increase the Number of Target processes for the manager
(ii) Change the cache size of the concurrent manager as this determines
how many requests will be evaluated by a manager at a time and should match the target (process) value as set above.
RELATED DOCUMENTS
-----------------
Note 1050938.6 What to Set $APPCPNAM for the Report Output File Naming Convention Format
Note 149600.1 FND_CONC_PP_ACTIONS and FND_RUN_REQ_PP_ACTIONS Growing Exponentially
Note 134007.1 CMCLEAN.SQL - Non Destructive Script to Clean Concurrent Manager Tables
PURPOSE
-------
To deliver a set of frequently asked questions against AOL FND Concurrent
Manager.
SCOPE & APPLICATION
-------------------
This reference would be most useful for one who is seeking additional
information regarding AOL FND Concurrent Manager issues.
FND Concurrent Manager FAQ's
-----------------------------
When would one be required to bounce (stop and restart) the Concurrent Manager?
When you modify the Printer Driver you have to restart the Manager which
runs the request which is attached to that Printer Driver, however,if you do
not know which manager then you have to restart the Internal manager because
the printer driver can be used by multiple managers and multiple requests.
If only a concurrent program definition is modified, running a verify on the
Internal Manager will pick up the changes without the need for bouncing the
manager.
Does the Internal manager schedule requests to be run or does it put requests
into queues to be run by other managers?
This is a very common misconception. The ICM really does not have any
such scheduling responsibilities. It has NOTHING to do with scheduling
requests, or deciding which manager will run a particular request.
Its function is only to run 'queue control' requests, which are
requests to startup or shutdown other managers. It is responsible for
startup and shutdown of the whole concurrent processing facility, and
it also monitors the other managers periodically, and restarts them if
they should go down. It can also take over the Conflict Resolution
manager's job, and resolve incompatibilities.
If the ICM itself should go down, requests will continue to run
normally, except for 'queue control' requests. You can restart it with
'startmgr', you do not need to kill the other managers first.
How can I check to see if a concurrent manager is running?
One way to see if a manager is running is to use the 'Administer
Concurrent Managers' form. Navigate to Concurrent->Managers->Administer.
You will see two columns labeled 'Actual' and 'Target'. The Target column
lists the number of processes that should be running for each manager
for this particular workshift. The Actual column lists the number of
processes that are actually running. If the Actual column is zero, there
are no processes running for this manager. If the Target column is zero,
then either a workshift has not been assigned to this manager, or the current
workshift does not specify any target processes. If the target column
is not zero, then the manager processes have either failed to start up,
or gone down. You should check the manager's logfile and the ICM
logfile. You can also search for OS processes using the 'ps' command.
It is possible for the form to be inaccurate, i.e. it may show actual
processes even though they are not really running. When in doubt, check for
processes at the OS level. On NT, you can check to see if the Concurrent Manager
service is running using the Services control panel.
Where do concurrent request or manager logfiles and output files go?
The concurrent manager first looks for the environment variable
$APPLCSF. If this is set, it creates a path using two other
environment variables: $APPLLOG and $APPLOUT
It places log files in $APPLCSF/$APPLLOG, output files go in
$APPLCSF/$APPLOUT
So for example, if you have this environment set:
$APPLCSF = /u01/appl/common
$APPLLOG = log
$APPLOUT = out
The concurrent manager will place log files in /u01/appl/common/log,
and output files in /u01/appl/common/out
Note that $APPLCSF must be a full, absolute path, and the other two
are directory names.
If $APPLCSF is not set, it places the files under the product top of
the application associated with the request. For example, a PO report
would go under $PO_TOP/$APPLLOG and $PO_TOP/$APPLOUT
Logfiles go to: /u01/appl/po/9.0/log
Output files to: /u01/appl/po/9.0/out
All these directories must exist and have the correct permissions.
Note that all concurrent requests produce a log file, but not necessarily
an output file.
Concurrent manager logfiles follow the same convention, and will be
found in the $APPLLOG directory
What are the logfile and output file naming conventions?
Request logfiles: l
Output files: If $APPCPNAM is not set:
If $APPCPNAM = REQID: o
If $APPCPNAM = USER:
Where:
And:
Manager logfiles:
ICM logfile: Default is std.mgr, can be changed with the mgrname
startup parameter
Concurrent manager log: w
Transaction manager log: t
Conflict Resolution manager log: c
Where:
Can I delete a concurrent manager?
You can disable the manager by checking the 'Enabled' checkbox, or
you can simply Terminate the manager and it will not run again unless
you reactivate it.
If it is really necessary, you can query the manager in the
'Define Manager' form, and delete the row. (It is recommended that you
DO NOT do this)
What is the function of the 'Conflict Resolution Manager'?
Concurrent managers read requests to start concurrent programs running. The
Conflict Resolution Manager checks concurrent program definitions for
incompatibility rules.
If a program is identified as Run Alone, then the Conflict Resolution Manager
prevents the concurrent managers from starting other programs in the same
conflict domain.
When a program lists other programs as being incompatible with it, the
Conflict Resolution Manager prevents the program from starting until any
incompatible programs in the same domain have completed running.
What is the 'Internal Scheduler/Prereleaser' manager?
The short name for this manager is FNDSCH. It is also known as the
Advanced Scheduler/Prereleaser Manager. This manager is intended
to implement Advanced Schedules. Its job is to determine when a
scheduled request is ready to run. Advanced Schedules were not fully
implemented in Release 11.0, they are implemented in Release 11.5,
but are not widely used by the various Apps products. General Ledger
uses FNDSCH for financial schedules based on different calendars and
period types. It is then possible to schedule AutoAllocation sets,
Recurring Journals, MassAllocations, Budget Formulas, and MassBudgets
to run according to the General Ledger schedules that have been
defined.
If financial schedules in GL are not being used then it is not a
problem to deactivate this manager.
What is the 'Internal Monitor' manager/service?
This manager/service is used to implement Distributed Concurrent Processing.
It monitors whether the ICM is still running, and if the ICM crashes,
it will restart it on another node.
You do not need to run this manager/service unless you are using Distributed
Concurrent Processing.
See the Installation manual and Sysadmin Guide for more info on DCP.
How do I check/set the PMON method?
To check the PMON method:
1) cd $FND_TOP/sql
2) sqlplus apps/apps @afimchk.sql
This will tell whether the internal manager is running, what the PMON
method is, and where the log file is.
To set the PMON method:
1) first shut the concurrent managers down
2) cd $FND_TOP/sql
3) sqlplus apps/apps @afimpmon.sql LOCK (or RDBMS)
How do I enable/disable the Conflict Resolution Manager?
Use the system profile option 'Concurrent: Use ICM'.
Setting this to 'No' (which is the default) allows the CRM to be started.
Setting it to 'Yes' causes the CRM to be shutdown and the Internal
Manager (ICM) will take over the conflict resolution duties. If the CRM will
not start (it is started automatically by the ICM), check this profile option.
Note that using the ICM to resolve conflicts is not recommended.
The CRM's sole purpose is to resolve conflicts, while the ICM has
other functions to perform as well. Only set this option to 'YES'
if you have a good reason to do so.
How do I clean out the Concurrent Manager tables?
Cleaning out the tables is a useful method of making sure that there
are no invalid statuses that can prevent the managers from starting.
Previously, this has been done by truncating fnd_concurrent_processes
and/or fnd_concurrent_requests. Truncation of the tables is a little
drastic, and can cause problems later when trying to purge requests,
not to mention losing all of the request information.
Run the script, cmclean.sql, article Note 134007.1 CMCLEAN.SQL - Non
Destructive Script to Clean Concurrent Manager Tables
It will make sure the relevant status codes are valid without
deleting any information.
How do I tell concurrent manager processes apart at the OS level?
Use: pf -ef | grep FNDLIBR
This will produce output like:
vd11 13703 13660 0 May 11 ? 0:01 FNDLIBR FND Concurrent_Processor
MANAGE OLOGIN="APPS/94A491A1000000000000000000
n1070161 24936 24927 0 Apr 29 ? 0:05 FNDLIBR FND Concurrent_Processor
MANAGE OLOGIN="APPS_APPDEMO/94C4B1C10000000000
n1070161 24938 24927 0 Apr 29 ? 0:06 FNDLIBR FND Concurrent_Processor
MANAGE OLOGIN="APPS_APPDEMO/94C4B1C10000000000
n1070161 24927 24922 0 Apr 29 ? 2:03 FNDLIBR FND CPMGR FNDCPMBR sysmgr
="" sleep=60 pmon=20 diag=N logfile=/u16/app
The last process, #24927, shows 'FNDLIBR FND CPMGR', this one is the
Internal Manager (ICM). Notice that it gives some of the parameters it
was started with, the other processes showing 'Concurrent_Processor'
are Standard manager processes. Notice that the ICM process is the
parent process of the Standard managers. (processes 24936 and 24938)
Other managers will have the name of the executable, like ARLIBR or
INVLIBR:
$ ps -ef | grep ARLIBR
vd11 13683 13660 0 May 11 ? 0:20 ARLIBR APPS/82A2A4940000000000000
000000000000000000000000000000000000000 AR ART
The Conflict Resolution manager will look like:
$ ps -ef | grep FNDCRM
n1070161 24941 24927 0 Apr 29 ? 1:17 FNDCRM APPS_APPDEMO/84BFBEB900000
0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
What is the syntax for controlling the concurrent manager using startmgr and
concsub in NT?
On NT, the concurrent manager is run as an NT service, you start and
stop the managers using the Services control panel.
See the Applications Installation manual for NT, Appendix A for
details. See pg. 5-9 of this manual for instructions on creating the
concurrent manager service.
Why am I seeing pinging entries like this in the ICM logfile?
PING (0.0.0.0): 56 data bytes
64 bytes from 192.75.91.2: icmp_seq=0 ttl=255 time=0.705 ms
64 bytes from 192.75.91.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=255 time=1.120 ms
Process monitor session ended : 29-FEB-2000 10:38:43
64 bytes from 192.75.91.2: icmp_seq=2 ttl=255 time=0.985 ms
64 bytes from 192.75.91.2: icmp_seq=3 ttl=255 time=1.006 ms
Pinging other machines is used in Distributed Concurrent Processing.
This means you have DCP turned on, using the environment variable
APPLDCP. Set APPLDCP to OFF and restart the managers.
I hit the Restart button to start the Standard manager, but it still did not
start?
Telling a manager to restart just sets the status to Restart. The ICM
will start it the next process monitor session or the next time the
ICM starts. Use Activate to start a manager immediately.
When a manager is deactivated manually, the ICM will not restart
it, you will need to set it to Restart, or activate it manually.
How many rows are in FND_CONCURRENT_REQUESTS and FND_CONCURRENT_PROCESSES
tables?
When tables reach above 3000-4000 rows, the performance begins to
diminish. You may want to run Purge Concurrent Request on a regular basis,
dependant on the amount of requests being run.
The Purge Concurrent Requests job can be used to purge:
Requests, Mgr logs, and All requests depending on what is chosen.
Use the following options: Enter = All, Mode = AGE, Mode Value = 15
The std.mgr log continuously grows where it may good to
archive it regularly.
Any processes pending in Internal or Conflict Resolution Manager?
Best course of action before starting the Concurrent Managers is to cancel
any "Deactivate" or "Verify" jobs pending in the Internal Manager and place
any other pending jobs on hold.
How do I turn on transaction manager diagnostics?
Set the profile option 'Concurrent:Debug Flags' to 'TCTM1' at the site
level. This will cause transactions to make debug entries in the
FND_CONCURRENT_DEBUG_INFO table. Truncate this table before running a
tranasction, then select the entries from the table.
Starting the managers with diag=Y will also produce more information
in the transaction manager logfile.
How do transaction managers work?
Briefly:
(See the server documentation for details on the DBMS_PIPE package)
1) A tranasction manager is started on the concurrent processing
server, and periodically reads the pipe for incoming transactions.
2) A client program (usually a form) calls the
FND_TRANSACTION.SYNCHRONOUS function.
3) This function writes a message into the pipe containing the program
to be run and its parameters.
4) FND_TRANSACTION.SYNCHRONOUS begins reading a return pipe for the
return status.
5) The manager sees the message in the pipe, retrieves the program id
and parameters.
6) The manager runs the program with the specified parameters. The
program will be of type 'Immediate', so there will not be a
separate concurrent request run.
7) The program completes, and the manager packs its return status into
the return pipe.
8) FND_TRANSACTION.SYNCHRONOUS reads the return value and passes it
back to its caller.
Note that these events take place essentially simultaneously on the
client and server. This is a synchronous transaction because the
client waits for the server to return, or times out waiting for it.
Problem....
When you try to submit a request like Active users or
Active responsibilities, request gets submitted.
When we view the help requests, you find that it is
inactive / nomanager.
Within 12 to 15 seconds, you refresh-it gets completed.
Initially, you could find only inactive and we look at
the diagnostic- the concurrent manager assigned is not
picking up.
There is no specialization rules in any managers except
the include program this source.
Solution....
Most often when this occurs where a request goes
"inactive/no manager" and is then processed a short time
later, the solution is to either increase the cache size
for your Standard manger, or increase the actual number of
Standard manager processes.
Cache Size is set on the CONCURRENT/MANAGER/DEFINE form. Basically,
this regulates how many requests a manager will pick up for each
sleep cycle.
How do I process more concurrent requests concurrently?
The Concurrent Manager parameters, (Query the concurrent manager by
Login as Sysadmin, navigate -> Concurrent -> Manager -> Define and Query for
the relevant concurrent manager), should be modified to handle more
concurrent requests concurrently, this can be done in two steps:
(i) Increase the Number of Target processes for the manager
(ii) Change the cache size of the concurrent manager as this determines
how many requests will be evaluated by a manager at a time and should match the target (process) value as set above.
RELATED DOCUMENTS
-----------------
Note 1050938.6 What to Set $APPCPNAM for the Report Output File Naming Convention Format
Note 149600.1 FND_CONC_PP_ACTIONS and FND_RUN_REQ_PP_ACTIONS Growing Exponentially
Note 134007.1 CMCLEAN.SQL - Non Destructive Script to Clean Concurrent Manager Tables
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)